Physical and Functional Interaction between 5-HT6 Receptor and Nova-1
- PMID: 30853821
- PMCID: PMC6401546
- DOI: 10.5607/en.2019.28.1.17
Physical and Functional Interaction between 5-HT6 Receptor and Nova-1
Abstract
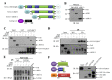
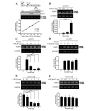
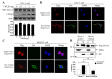
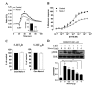
5-HT6 receptor (5-HT6R) is implicated in cognitive dysfunction, mood disorder, psychosis, and eating disorders. However, despite its significant role in regulating the brain functions, regulation of 5-HT6R at the molecular level is poorly understood. Here, using yeast two-hybrid assay, we found that human 5-HT6R directly binds to neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 (Nova-1), a brain-enriched splicing regulator. The interaction between 5-HT6R and Nova-1 was confirmed using GST pull-down and co-immunoprecipitation assays in cell lines and rat brain. The splicing activity of Nova-1 was decreased upon overexpression of 5-HT6R, which was examined by detecting the spliced intermediates of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), a known pre-mRNA target of Nova-1, using RT-PCR. In addition, overexpression of 5-HT6R induced the translocation of Nova-1 from the nucleus to cytoplasm, resulting in the reduced splicing activity of Nova-1. In contrast, overexpression of Nova-1 reduced the activity and the total protein levels of 5-HT6R. Taken together, these results indicate that when the expression levels of 5-HT6R or Nova-1 protein are not properly regulated, it may also deteriorate the function of the other.
Keywords: 5-HT6 receptor; Neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1; Neurological diseases; RNA binding proteins; Serotonin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nova-1 mediates glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of pre-mRNA splicing of gonadotropin-releasing hormone transcripts.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 8;284(19):12792-800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807386200. Epub 2009 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19282286 Free PMC article.
-
Direct interaction and functional coupling between human 5-HT6 receptor and the light chain 1 subunit of the microtubule-associated protein 1B (MAP1B-LC1).PLoS One. 2014 Mar 10;9(3):e91402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091402. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24614691 Free PMC article.
-
A brain-enriched polypyrimidine tract-binding protein antagonizes the ability of Nova to regulate neuron-specific alternative splicing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 6;97(12):6350-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.110128397. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10829067 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT6 Receptor: A New Player Controlling the Development of Neural Circuits.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):951-60. doi: 10.1021/cn500326z. Epub 2015 Jan 28. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25590789 Review.
-
5-HT6 Receptor Antagonists: Potential Efficacy for the Treatment of Cognitive Impairment in Schizophrenia.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(26):3739-59. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150605112105. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26044973 Review.
Cited by
-
The 5-HT6 Receptors in the Ventrolateral Orbital Cortex Attenuate Allodynia in a Rodent Model of Neuropathic Pain.Front Neurosci. 2020 Aug 18;14:884. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00884. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32973437 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Splicing by NOVA Factors: From Gene Expression to Cell Physiology and Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 30;21(11):3941. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113941. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32486302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-HT6 receptors: Contemporary views on their neurobiological and pharmacological relevance in neuropsychiatric disorders.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2025 Dec;27(1):112-128. doi: 10.1080/19585969.2025.2502028. Epub 2025 May 10. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40347153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, Hartig PR, Martin GR, Mylecharane EJ, Saxena PR, Humphrey PP. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) Pharmacol Rev. 1994;46:157–203. - PubMed
-
- Kohen R, Metcalf MA, Khan N, Druck T, Huebner K, Lachowicz JE, Meltzer HY, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Hamblin MW. Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a human 5-HT6 serotonin receptor. J Neurochem. 1996;66:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Ruat M, Traiffort E, Arrang JM, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Diaz J, Leurs R, Schwartz JC. A novel rat serotonin (5-HT6) receptor: molecular cloning, localization and stimulation of cAMP accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;193:268–276. - PubMed
-
- Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Fone KC. 5-ht6 receptors. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004;3:59–79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

