REMODEL: Rethinking Deep CNN Models to Detect and Count on a NeuroSynaptic System
- PMID: 30853879
- PMCID: PMC6395404
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00004
REMODEL: Rethinking Deep CNN Models to Detect and Count on a NeuroSynaptic System
Abstract
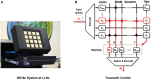
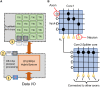
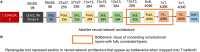
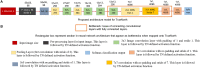
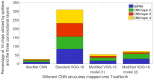
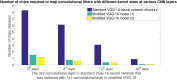
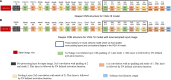
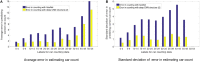
In this work, we perform analysis of detection and counting of cars using a low-power IBM TrueNorth Neurosynaptic System. For our evaluation we looked at a publicly-available dataset that has overhead imagery of cars with context present in the image. The trained neural network for image analysis was deployed on the NS16e system using IBM's EEDN training framework. Through multiple experiments we identify the architectural bottlenecks present in TrueNorth system that does not let us deploy large neural network structures. Following these experiments we propose changes to CNN model to circumvent these architectural bottlenecks. The results of these evaluations have been compared with caffe-based implementations of standard neural networks that were deployed on a Titan-X GPU. Results showed that TrueNorth can detect cars from the dataset with 97.60% accuracy and can be used to accurately count the number of cars in the image with 69.04% accuracy. The car detection accuracy and car count (-/+ 2 error margin) accuracy are comparable to high-precision neural networks like AlexNet, GoogLeNet, and ResCeption, but show a manifold improvement in power consumption.
Keywords: IBM TrueNorth Neurosynaptic System; aerial image analysis; convolutional neural network; deep learning; neuromorphic computing; spiking neural network.
Figures




References
-
- Akopyan F., Sawada J., Cassidy A., Alvarez-Icaza R., Arthur J., Merolla P., et al. (2015). Truenorth: design and tool flow of a 65 mw 1 million neuron programmable neurosynaptic chip. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 34, 1537–1557. 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2474396 - DOI
-
- Alom M. Z., Josue T., Rahman M. N., Mitchell W., Yakopcic C., Taha T. M. (2018). Deep versus wide convolutional neural networks for object recognition on neuromorphic system, in 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (Rio de Janeiro: ), 1–8. 10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489635 - DOI
-
- Cao Y., Chen Y., Khosla D. (2015). Spiking deep convolutional neural networks for energy-efficient object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vision 113, 54–66. 10.1007/s11263-014-0788-3 - DOI
-
- Cassidy A. S., Merolla P., Arthur J. V., Esser S. K., Jackson B., Alvarez-Icaza R., et al. (2013). Cognitive computing building block: A versatile and efficient digital neuron model for neurosynaptic cores, in The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (Dallas, TX: ), 1–10. 10.1109/IJCNN.2013.6707077 - DOI
-
- Clawson T. S., Ferrari S., Fuller S. B., Wood R. J. (2016). Spiking neural network (SNN) control of a flapping insect-scale robot, in 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) (Las Vegas, NV: ), 3381–3388. 10.1109/CDC.2016.7798778 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

