Cell Type-Specific Human APP Transgene Expression by Hippocampal Interneurons in the Tg2576 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30853883
- PMCID: PMC6395433
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00137
Cell Type-Specific Human APP Transgene Expression by Hippocampal Interneurons in the Tg2576 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
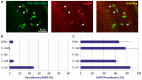
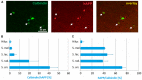
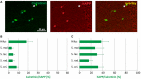
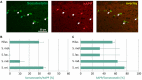
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) transgenic animal models of Alzheimer's disease have become versatile tools for basic and translational research. However, there is great heterogeneity of histological, biochemical, and functional data between transgenic mouse lines, which might be due to different transgene expression patterns. Here, the expression of human APP (hAPP) by GABAergic hippocampal interneurons immunoreactive for the calcium binding proteins parvalbumin, calbindin, calretinin, and for the peptide hormone somatostatin was analyzed in Tg2576 mice by double immunofluorescent microscopy. Overall, there was no GABAergic interneuron subpopulation that did not express the transgene. On the other hand, in no case all neurons of such a subpopulation expressed hAPP. In dentate gyrus molecular layer and in stratum lacunosum moleculare less than 10% of hAPP-positive interneurons co-express any of these interneuron markers, whereas in stratum oriens hAPP-expressing neurons frequently co-express these interneuron markers to different proportions. We conclude that these neurons differentially contribute to deficits in young Tg2576 mice before the onset of Abeta plaque pathology. The detailed analysis of distinct brain region and neuron type-specific APP transgene expression patterns is indispensable to understand particular pathological features and mouse line-specific differences in neuronal and systemic functions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid precursor protein; animal model; calcium-binding proteins; hippocampus; interneuron.
Figures


References
-
- Baglietto-Vargas D., Moreno-Gonzalez I., Sanchez-Varo R., Jimenez S., Trujillo-Estrada L., Sanchez-Mejias E., et al. (2010). Calretinin interneurons are early targets of extracellular amyloid-beta pathology in PS1/AbetaPP Alzheimer mice hippocampus. J. Alzheimers Dis. 21 119–132. 10.3233/JAD-2010-100066 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

