Cycling Quiescence in Temozolomide Resistant Glioblastoma Cells Is Partly Explained by microRNA-93 and -193-Mediated Decrease of Cyclin D
- PMID: 30853911
- PMCID: PMC6395452
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00134
Cycling Quiescence in Temozolomide Resistant Glioblastoma Cells Is Partly Explained by microRNA-93 and -193-Mediated Decrease of Cyclin D
Abstract
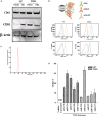
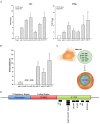
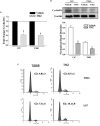
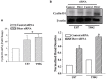
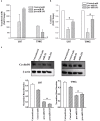
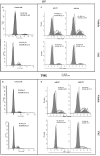
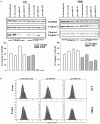
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a fatal malignancy of the central nervous system, commonly associated with chemoresistance. The alkylating agent Temozolomide (TMZ) is the front-line chemotherapeutic agent and has undergone intense studies on resistance. These studies reported on mismatch repair gene upregulation, ABC-targeted drug efflux, and cell cycle alterations. The mechanism by which TMZ induces cell cycle arrest has not been well-established. TMZ-resistant GBM cells have been linked to microRNA (miRNA) and exosomes. A cell cycle miRNA array identified distinct miRNAs only in exosomes from TMZ-resistant GBM cell lines and primary spheres. We narrowed the miRs to miR-93 and -193 and showed in computational analyses that they could target Cyclin D1. Since Cyclin D1 is a major regulator of cell cycle progression, we performed cause-effect studies and showed a blunting effects of miR-93 and -193 in Cyclin D1 expression. These two miRs also decreased cell cycling quiescence and induced resistance to TMZ. Taken together, our data provide a mechanism by which GBM cells can exhibit TMZ-induced resistance through miRNA targeting of Cyclin D1. The data provide a number of therapeutic approaches to reverse chemoresistance at the miRNA, exosomal and cell cycle points.
Keywords: Cyclin D; cell cycle; chemoresistance; glioblastoma; microRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomal transfer of miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in drug-resistant glioblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2018 Nov 1;436:10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.004. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30102952
-
Exosomal transfer of miR-1238 contributes to temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma.EBioMedicine. 2019 Apr;42:238-251. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 Mar 24. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30917935 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cyclin E1 overcomes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma by Mcl-1 degradation.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Aug;58(8):1502-1511. doi: 10.1002/mc.23034. Epub 2019 May 2. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31045274
-
Exosomal transfer of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 enhances chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 16;38(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1139-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30992025 Free PMC article.
-
Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme.Genes Dis. 2016 May 11;3(3):198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2016.04.007. eCollection 2016 Sep. Genes Dis. 2016. PMID: 30258889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in acquisition of resistance to therapy in glioblastomas.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021 Mar 19;4(1):1-16. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.61. eCollection 2021. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 35582008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal connexin 43 regulates the resistance of glioma cells to temozolomide.Oncol Rep. 2021 Apr;45(4):44. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7995. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649836 Free PMC article.
-
The epigenetic mechanisms involved in the treatment resistance of glioblastoma.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 13;8:12. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.157. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40201311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Intercell Communication between Glioblastoma and Microenvironment through Extracellular Vesicles.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 11;10(1):151. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010151. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35052830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Forging New Therapeutic Targets: Efforts of Tumor Derived Exosomes to Prepare the Pre-Metastatic Niche for Cancer Cell Dissemination and Dormancy.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 1;11(6):1614. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061614. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

