Identification and characterization of dysregulated P-element induced wimpy testis-interacting RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 30854037
- PMCID: PMC6365962
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.9913
Identification and characterization of dysregulated P-element induced wimpy testis-interacting RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
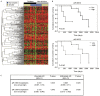
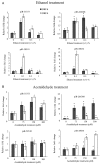
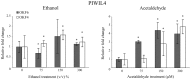
It is clear that alcohol consumption is a major risk factor in the pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); however, the molecular mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of alcohol-associated HNSCC remains poorly understood. The aim of the present study was to identify and characterize P-element-induced wimpy testis (PIWI)-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) and PIWI proteins dysregulated in alcohol-associated HNSCC to elucidate their function in the development of this cancer. Using next generation RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data obtained from 40 HNSCC patients, the piRNA and PIWI protein expression of HNSCC samples was compared between alcohol drinkers and non-drinkers. A separate piRNA expression RNA-seq analysis of 18 non-smoker HNSCC patients was also conducted. To verify piRNA expression, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was performed on the most differentially expressed alcohol-associated piRNAs in ethanol and acetaldehyde-treated normal oral keratinocytes. The correlation between piRNA expression and patient survival was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier estimators and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models. A comparison between alcohol drinking and non-drinking HNSCC patients demonstrated that a panel of 3,223 piRNA transcripts were consistently detected and differentially expressed. RNA-seq analysis and in vitro RT-qPCR verification revealed that 4 of these piRNAs, piR-35373, piR-266308, piR-58510 and piR-38034, were significantly dysregulated between drinking and non-drinking cohorts. Of these four piRNAs, low expression of piR-58510 and piR-35373 significantly correlated with improved patient survival. Furthermore, human PIWI-like protein 4 was consistently upregulated in ethanol and acetaldehyde-treated normal oral keratinocytes. These results demonstrate that alcohol consumption may cause dysregulation of piRNA expression in HNSCC and in vitro verifications identified 4 piRNAs that may be involved in the pathogenesis of alcohol-associated HNSCC.
Keywords: alcohol; epigenetics; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; piwi-interacting RNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HPV status is associated with altered PIWI-interacting RNA expression pattern in head and neck cancer.Oral Oncol. 2016 Apr;55:43-48. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26852287 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and role of P-element-induced wimpy testis-interacting RNA in diabetic-retinopathy in mice.World J Diabetes. 2021 Jul 15;12(7):1116-1130. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.1116. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34326959 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-seq analysis identifies key long non-coding RNAs connected to the pathogenesis of alcohol-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2016 Oct;12(4):2846-2853. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4972. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27698869 Free PMC article.
-
Piwi-Interacting RNAs: A New Class of Regulator in Human Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 6;11:695077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.695077. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34295823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic roles of PIWI proteins and piRNAs in lung cancer.Cell Biosci. 2019 Dec 21;9:102. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0368-x. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31890151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PIWI-interacting RNAs (PiRNAs) as emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets in biliary tract cancers: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(13):e33767. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33767. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIWI-interacting RNAs: Mitochondria-based biogenesis and functions in cancer.Genes Dis. 2020 Oct 5;8(5):603-622. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.09.006. eCollection 2021 Sep. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 34291132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging functions of piwi-interacting RNAs in diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(11):4893-4901. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16466. Epub 2021 May 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33942984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of piRNAs in cancer: challenges and prospects.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Nov 13;11(21):9932-9946. doi: 10.18632/aging.102417. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31727866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Biogenesis and Functions of piRNAs in Human Diseases.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 4;21:108-120. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.05.023. Epub 2020 May 23. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32516734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Silveira NJ, Varuzza L, Machado-Lima A, Lauretto MS, Pinheiro DG, Rodrigues RV, Severino P, Nobrega FG, Head and Neck Genome Project GENCAPO. Silva WA, Jr, et al. Searching for molecular markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) by statistical and bioinformatic analysis of larynx-derived SAGE libraries. BMC Med Genomics. 2008;1:56. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-1-56. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hashibe M, Brennan P, Benhamou S, Castellsague X, Chen C, Curado MP, Dal Maso L, Daudt AW, Fabianova E, Fernandez L, et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:777–789. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk179. - DOI - PubMed
