Molecular mechanism of triple-negative breast cancer-associated BRCA1 and the identification of signaling pathways
- PMID: 30854067
- PMCID: PMC6365902
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.9884
Molecular mechanism of triple-negative breast cancer-associated BRCA1 and the identification of signaling pathways
Abstract
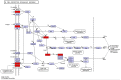
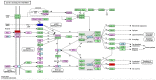
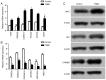
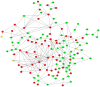
BRAC1 has multiple important interactions with triple-negative breast cancer, the specific molecular characteristics of this interaction, however, have not yet been completely elucidated. By examining cell signaling pathways, important information for comprehending the potential mechanisms of this cancer may become known. The aim of the present study was to identify the effects of BRAC1 and to find the signaling pathway(s) involved in the pathogenic mechanism of triple-negative breast cancer. In this study, GSE27447 microarray data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information, and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from GSE27447 were distinguished by Significant Analysis of Microarray. Gene ontology (GO) analysis was carried out on 132 upregulated and 198 downregulated genes with DAVID. The signaling was forecast by the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Transcription factors were recognized by TFatS. The BRAC1 relevant protein-protein interaction networks (PPI) were fixed by STRING and visualized by CytoScape. Overall, the upregulated DEGs, which included CR2, IGHM, PRKCB, CARD11, PLCG2, CD79A, IGKC and CD27, were primarily enriched in the terms associated with immune responses, and the downregulated DEGs, which included STARD3, ALDH8A1, SRD5A3, CACNA1H, UGT2B4, SDR16C5 and MED1, were primarily enriched in the hormone metabolic process. In addition, 13 pathways, such as the B-cell receptor-signaling pathway, the hormone synthesis signaling pathway and the oxytocin-signaling pathway, were chosen. MYC, SP1 and CTNNB1 were determined to be enriched in triple-negative breast cancer. A total of 8 genes were identified to be downregulated in the BRAC1-related PPI network. The results of the present study show a fresh angle on the molecular mechanism of triple-negative breast cancer and indicate a possible target for its treatment.
Keywords: differentially expressed genes; gene ontology analysis; protein-protein interaction network; signaling pathway; triple-negative breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Chu J, Bae H, Seo Y, Cho SY, Kim SH, Cho EY. The prognostic impact of synchronous ipsilateral multiple breast cancer: Survival Outcomes according to the Eighth American Joint Committee on cancer staging and molecular subtype. J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52:396–403. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2018.10.03. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zubeda S, Kaipa PR, Shaik NA, Mohiuddin MK, Vaidya S, Pavani B, Srinivasulu M, Latha MM, Hasan Q. Her-2/neu status: A neglected marker of prognostication and management of patients with breast cancer in India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2231–2235. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.4.2231. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer. 2010;109:1721–1728. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22618. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
