Topical, systemic and biologic therapies in hidradenitis suppurativa: pathogenic insights by examining therapeutic mechanisms
- PMID: 30854183
- PMCID: PMC6399757
- DOI: 10.1177/2040622319830646
Topical, systemic and biologic therapies in hidradenitis suppurativa: pathogenic insights by examining therapeutic mechanisms
Abstract
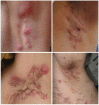
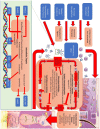
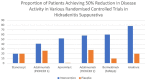
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the skin, manifesting in chronic, recurrent painful pustules, nodules, boils and purulent draining abscesses. Our current understanding of the pathogenesis of the disease is incomplete. This review aims to identify available treatment options in HS and discuss the pharmacological mechanisms through which such agents function. Identifying common pathways may inform our understanding of the pathogenesis of HS as well as identify future therapeutic targets. The pharmacological mechanisms implicated in topical therapies, antibiotic, hormonal, systemic immunomodulatory and biologic therapies for HS are discussed. Significant differences exist between agents and implicated pathways in therapy for mild and severe disease. This is an expression of the possible dichotomy in inflammatory pathways (and treatment responses) in HS. Studies involving monoclonal antibodies provide the greatest insight into what these specific mechanisms may be. Their variable levels of clinical efficacy compared with placebo bolsters the suggestion that differential inflammatory pathways may be involved in different presentations and severity of disease. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and other innate immune mechanisms are strongly represented in treatments which are effective in mild to moderate disease in the absence of scarring or draining fistulae, however complex feed-forward mechanisms in severe disease respond to interleukin (IL)-1 inhibition but are less likely to respond to innate immune inhibition (through NF-κB or TNF-α) alone. It is unclear whether IL-17 inhibition will parallel TNF-α or IL-1 inhibition in effect, however it is plausible that small molecule targets (Janus kinase1 and phosphodiesterase 4) may provide effective new strategies for treatment of HS.
Keywords: biologics; cytokines; hidradenitis suppurativa; inflammation; interleukin-17; tetracycline; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: JEH serves as an investigator/consultant for Pfizer Inc. and Novartis. JGK has been a consultant to, and has received research support from, the following companies that have developed or are developing therapeutics for psoriasis: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer, Bristol–Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Idera, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Serono, Sun, Valeant, and Vitae. The other authors have no financial conflicts of interest
Figures
References
-
- Hoffman LK, Ghias MH, Lowes MA. Pathophysiology of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Semin Cutan Med Surg 2017; 36: 47–54. - PubMed
-
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based clinical practice research datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol 2018; 178: 917–924. - PubMed
-
- Frew JW, Vekic DA, Woods JA, et al. A systematic review and critical evaluation of reported pathogenic sequence variants in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol 2017; 177: 987–998. - PubMed
-
- Kirby JS, Miller JJ, Adams DR, et al. Healthcare utilization patterns and costs for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol 2014; 150: 937–944. - PubMed
-
- Saunte DM, Boer J, Stratigos A, et al. Diagnostic delay in hidradenitis suppurativa is a global problem. Br J Dermatol 2015; 173: 1546–1549. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

