Polymorphism rs2395655 affects LEDGF/p75 binding activity and p21WAF1/CIP1 gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 30854807
- PMCID: PMC6536968
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2067
Polymorphism rs2395655 affects LEDGF/p75 binding activity and p21WAF1/CIP1 gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
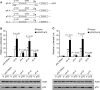
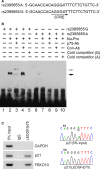
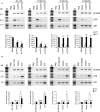
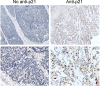
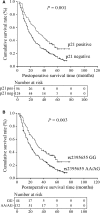
p21WAF1/CIP1 (p21) plays critical roles in cell-cycle regulation and DNA repair and is transcriptionally regulated through p53-dependent or -independent pathways. Bioinformatic analysis predicated one stress-response element (STRE) implicated in single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs2395655 of the p21 promoter. Here, we investigated the transcriptional regulatory function of rs2395655 variant genotype and analyzed its associations with the p21 expression and clinical outcomes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients. Luciferase assay results showed significantly increased transcriptional activity of the rs2395655 G allele-containing p21 promoter compared with rs2395655 A allele-containing counterpart, especially in ESCC cells with ectopic LEDGF/p75 expression. Furthermore electrophoretic mobility shift assay using the rs2395655 G or A allele-containing probe and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay with specific anti-LEDGF/p75 antibody indicated the potential binding activity of LEDGF/p75 with the STRE element implicated in rs2395655 G allele of the p21 promoter. Subsequent specific RNA interference-mediated depletion or ectopic expression of LEDGF/p75 caused obviously down- or up-regulated expression of p21 mRNA in ESCC cells harboring rs2395655 GG genotype but not cells with rs2395655 AA genotype. Furthermore, rs2395655 GG genotype carriers showed significantly elevated p21 protein expression and conferred survival advantage in both univariate and multivariate analyses in total 218 ESCC patients. Our findings suggest that LEDGF/p75 regulates the p21 expression in ESCC cells through interacting with STRE element implicated in polymorphism rs2395655 and the elevated p21 protein expression and rs2395655 GG genotype may serve as positive prognostic factors for ESCC patients.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; lens epithelium-derived growth factor; p21WAF1/CIP1; prognostic factor; single-nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69‐90. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277‐300. - PubMed
-
- Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, et al. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993;366:701‐704. - PubMed
-
- Sarbia M, Stahl M, Zur Hausen A, et al. Expression of p21WAF1 predicts outcome of esophageal cancer patients treated by surgery alone or by combined therapy modalities. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:2615‐2623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

