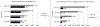Using life history calendars to improve measurement of lifetime experience with mental disorders
- PMID: 30854987
- PMCID: PMC6739186
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291719000394
Using life history calendars to improve measurement of lifetime experience with mental disorders
Abstract
Background: Retrospective reports of lifetime experience with mental disorders greatly underestimate the actual experiences of disorder because recall error biases reporting of earlier life symptoms downward. This fundamental obstacle to accurate reporting has many adverse consequences for the study and treatment of mental disorders. Better tools for accurate retrospective reporting of mental disorder symptoms have the potential for broad scientific benefits.
Methods: We designed a life history calendar (LHC) to support this task, and randomized more than 1000 individuals to each arm of a retrospective diagnostic interview with and without the LHC. We also conducted a careful validation with the Structured Clinical Interview for the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-Fourth Edition.
Results: Results demonstrate that-just as with frequent measurement longitudinal studies-use of an LHC in retrospective measurement can more than double reports of lifetime experience of some mental disorders.
Conclusions: The LHC significantly improves retrospective reporting of mental disorders. This tool is practical for application in both large cross-sectional surveys of the general population and clinical intake of new patients.
Keywords: CIDI; Life History Calendar; disorder under-reporting; lifetime prevalence; recall; retrospective reporting.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
Dr. Ghimire is also the Director of the Institute for Social and Environmental Research in Nepal (ISER-N) that collected the data for the research reported here. Dr. Ghimire’s conflict of interest management plan is approved and monitored by the Regents of the University of Michigan.
Figures
References
-
- Axinn WG, Barber JS, Ghimire DJ (1997). The Neighborhood History Calendar: A Data Collection Method Designed for Dynamic Multilevel Modeling. Sociological Methodology 27, 355–392. - PubMed
-
- Axinn WG, Pearce LD (2006). Mixed Method Data Collection Strategies. Cambridge University Press: New York, NY.