Screening and purification of nanobodies from E. coli culture supernatants using the hemolysin secretion system
- PMID: 30857538
- PMCID: PMC6410518
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-019-1094-0
Screening and purification of nanobodies from E. coli culture supernatants using the hemolysin secretion system
Abstract
Background: The hemolysin (Hly) secretion system of E. coli allows the one-step translocation of hemolysin A (HlyA) from the bacterial cytoplasm to the extracellular medium, without a periplasmic intermediate. In this work, we investigate whether the Hly secretion system of E. coli is competent to secrete a repertoire of functional single-domain VHH antibodies (nanobodies, Nbs), facilitating direct screening of VHH libraries and the purification of selected Nb from the extracellular medium.
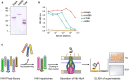
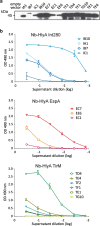
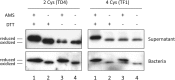
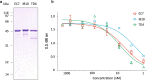
Results: We employed a phagemid library of VHHs obtained by immunization of a dromedary with three protein antigens from enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC), namely, the extracellular secreted protein A (EspA), the extracellular C-terminal region of Intimin (Int280), and the translocated intimin receptor middle domain (TirM). VHH clones binding each antigen were enriched and amplified by biopanning, and subsequently fused to the C-terminal secretion signal of HlyA to be expressed and secreted in a E. coli strain carrying the Hly export machinery (HlyB, HlyD and TolC). Individual E. coli clones were grown and induced in 96-well microtiter plates, and the supernatants of the producing cultures directly used in ELISA for detection of Nbs binding EspA, Int280 and TirM. A set of Nb sequences specifically binding each of these antigens were identified, indicating that the Hly system is able to secrete a diversity of functional Nbs. We performed thiol alkylation assays demonstrating that Nbs are correctly oxidized upon secretion, forming disulphide bonds between cysteine pairs despite the absence of a periplasmic intermediate. In addition, we show that the secreted Nb-HlyA fusions can be directly purified from the supernatant of E. coli cultures, avoiding cell lysis and in a single affinity chromatography step.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate the Hly secretion system of E. coli can be used as an expression platform for screening and purification of Nb binders from VHH repertories.
Keywords: E. coli/hemolysin; Nanobodies; Protein secretion; Single-domain antibodies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL 933.Infect Immun. 1995 Mar;63(3):1055-61. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.3.1055-1061.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7868227 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of disulphide bonds during secretion of proteins through the periplasmic-independent type I pathway.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Apr;40(2):332-46. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02410.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11309117
-
Identification of Nanobodies Blocking Intimate Adherence of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli to Epithelial Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2291:253-272. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1339-9_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33704757
-
Hemolysin of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli: structure, transport, biological activity and putative role in virulence.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Jul;304(5-6):521-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 May 15. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24933303 Review.
-
A novel C-terminal signal sequence targets Escherichia coli haemolysin directly to the medium.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;11:45-57. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.4. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989. PMID: 2693460 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant expression of nanobodies and nanobody-derived immunoreagents.Protein Expr Purif. 2020 Aug;172:105645. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2020.105645. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Protein Expr Purif. 2020. PMID: 32289357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A whole-cell platform for discovering synthetic cell adhesion molecules in bacteria.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 3;15(1):6568. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51017-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39095377 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted bacterial conjugation mediated by synthetic cell-to-cell adhesions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Dec 9;50(22):12938-12950. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1164. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36511856 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Hemolysin Type 1 Secretion System in Escherichia coli by Directed Evolution of the Hly Enhancer Fragment and Including a Terminator Region.Chembiochem. 2022 Mar 18;23(6):e202100702. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100702. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35062047 Free PMC article.
-
NANOBODIES®: A Review of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):5994. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065994. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36983063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

