Functional proteomic atlas of HIV infection in primary human CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 30857592
- PMCID: PMC6414203
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.41431
Functional proteomic atlas of HIV infection in primary human CD4+ T cells
Abstract
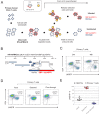
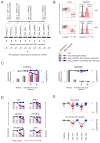
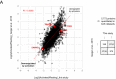
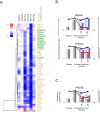
Viruses manipulate host cells to enhance their replication, and the identification of cellular factors targeted by viruses has led to key insights into both viral pathogenesis and cell biology. In this study, we develop an HIV reporter virus (HIV-AFMACS) displaying a streptavidin-binding affinity tag at the surface of infected cells, allowing facile one-step selection with streptavidin-conjugated magnetic beads. We use this system to obtain pure populations of HIV-infected primary human CD4+ T cells for detailed proteomic analysis, and quantitate approximately 9000 proteins across multiple donors on a dynamic background of T cell activation. Amongst 650 HIV-dependent changes (q < 0.05), we describe novel Vif-dependent targets FMR1 and DPH7, and 192 proteins not identified and/or regulated in T cell lines, such as ARID5A and PTPN22. We therefore provide a high-coverage functional proteomic atlas of HIV infection, and a mechanistic account of host factors subverted by the virus in its natural target cell.
Keywords: HIV; human; immunology; infectious disease; inflammation; magnetic cell selection; microbiology; primary human CD4+ T cell; proteomics; virus.
© 2019, Naamati et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AN, JW, EG, SM, PL, NM No competing interests declared
Figures



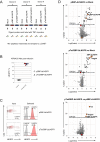
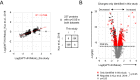
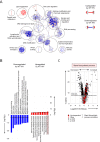
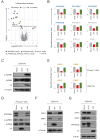
Similar articles
-
In Vivo and in Vitro Proteome Analysis of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-1-infected, Human CD4+ T Cells.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Apr;16(4 suppl 1):S108-S123. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.065235. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28223351 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal proteomic analysis of HIV infection reveals remodelling of the host phosphoproteome by lentiviral Vif variants.Elife. 2016 Sep 30;5:e18296. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18296. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27690223 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular APOBEC3G restricts HIV-1 infection in resting CD4+ T cells.Nature. 2005 May 5;435(7038):108-14. doi: 10.1038/nature03493. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Nature. 2005. Retraction in: Nature. 2010 Jul 8;466(7303):276. doi: 10.1038/nature09254. PMID: 15829920 Retracted.
-
Complementation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vif mutants in some CD4+ T-cell lines.Virus Res. 1994 Sep;33(3):269-80. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(94)90108-2. Virus Res. 1994. PMID: 7527173
-
The role of Vif during HIV-1 infection: interaction with novel host cellular factors.J Clin Virol. 2003 Feb;26(2):143-52. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(02)00113-0. J Clin Virol. 2003. PMID: 12600646 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral factors and their counteraction by HIV-1: many uncovered and more to be discovered.J Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Jul 29;16(2):mjae005. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae005. J Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38318650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV and Proteomics: What We Have Learned from High Throughput Studies.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021 Jan;15(1):e2000040. doi: 10.1002/prca.202000040. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021. PMID: 32978881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Cycle Regulation in Macrophages and Susceptibility to HIV-1.Viruses. 2020 Jul 31;12(8):839. doi: 10.3390/v12080839. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32751972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of T Cell Signaling and Immune Responses by PTPN22.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(10):443-452. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2378810. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39039893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of T-Cell Spatial Proteomics and the Influence of HIV Expression.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022 Mar;21(3):100194. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2022.100194. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35017099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apps R, Del Prete GQ, Chatterjee P, Lara A, Brumme ZL, Brockman MA, Neil S, Pickering S, Schneider DK, Piechocka-Trocha A, Walker BD, Thomas R, Shaw GM, Hahn BH, Keele BF, Lifson JD, Carrington M. HIV-1 vpu mediates HLA-C downregulation. Cell Host & Microbe. 2016;19:686–695. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.04.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arthos J, Cicala C, Martinelli E, Macleod K, Van Ryk D, Wei D, Xiao Z, Veenstra TD, Conrad TP, Lempicki RA, McLaughlin S, Pascuccio M, Gopaul R, McNally J, Cruz CC, Censoplano N, Chung E, Reitano KN, Kottilil S, Goode DJ, Fauci AS. HIV-1 envelope protein binds to and signals through integrin alpha4beta7, the gut mucosal homing receptor for peripheral T cells. Nature Immunology. 2008;9:301–309. doi: 10.1038/ni1566. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

