Alteration of 28S rRNA 2'- O-methylation by etoposide correlates with decreased SMN phosphorylation and reduced Drosha levels
- PMID: 30858166
- PMCID: PMC6451326
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.041848
Alteration of 28S rRNA 2'- O-methylation by etoposide correlates with decreased SMN phosphorylation and reduced Drosha levels
Abstract
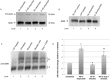
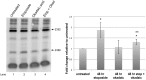
The most common types of modification in human rRNA are pseudouridylation and 2'-O ribose methylation. These modifications are performed by small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (snoRNPs) which contain a guide RNA (snoRNA) that base pairs at specific sites within the rRNA to direct the modification. rRNA modifications can vary, generating ribosome heterogeneity. One possible method that can be used to regulate rRNA modifications is by controlling snoRNP activity. RNA fragments derived from some small Cajal body-specific RNAs (scaRNA 2, 9 and 17) may influence snoRNP activity. Most scaRNAs accumulate in the Cajal body - a subnuclear domain - where they participate in the biogenesis of small nuclear RNPs, but scaRNA 2, 9 and 17 generate nucleolus-enriched fragments of unclear function, and we hypothesize that these fragments form regulatory RNPs that impact snoRNP activity and modulate rRNA modifications. Our previous work has shown that SMN, Drosha and various stresses, including etoposide treatment, may alter regulatory RNP formation. Here we demonstrate that etoposide treatment decreases the phosphorylation of SMN, reduces Drosha levels and increases the 2'-O-methylation of two sites within 28S rRNA. These findings further support a role for SMN and Drosha in regulating rRNA modification, possibly by affecting snoRNP or regulatory RNP activity.
Keywords: Cajal body; Drosha; SMN; rRNA modification; snoRNP.
© 2019. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

