Clinical Data on Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline versus Standard of Care Monotherapy in the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
- PMID: 30858203
- PMCID: PMC6496065
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02483-18
Clinical Data on Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline versus Standard of Care Monotherapy in the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
Abstract
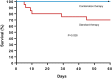
Vancomycin (VAN) and daptomycin (DAP) are approved as a monotherapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteremia. A regimen of daptomycin plus ceftaroline (DAP+CPT) has shown promise in published case series of MRSA salvage therapy, but no comparative data exist to compare up-front DAP+CPT head-to-head therapy versus standard monotherapy as an initial treatment. In a pilot study, we evaluated 40 adult patients who were randomized to receive 6 to 8 mg/kg of body weight per day of DAP and 600 mg intravenous (i.v.) CPT every 8 h (q8h) (n = 17) or standard monotherapy (n = 23) with vancomycin (VAN; dosed to achieve serum trough concentrations of 15 to 20 mg/liter; n = 21) or 6 to 8 mg/kg/day DAP (n = 2). Serum drawn on the first day of bacteremia was sent to a reference laboratory post hoc for measurement of interleukin-10 (IL-10) concentrations and correlation to in-hospital mortality. Sources of bacteremia, median Pitt bacteremia scores, Charlson comorbidity indices, and median IL-10 serum concentrations were similar in both groups. Although the study was initially designed to examine bacteremia duration, we observed an unanticipated in-hospital mortality difference of 0% (0/17) for combination therapy and 26% (6/23) for monotherapy (P = 0.029), causing us to halt the study. Among patients with an IL-10 concentration of >5 pg/ml, 0% (0/14) died in the DAP+CPT group versus 26% (5/19) in the monotherapy group (P = 0.057). Here, we share the full results of this preliminary (but aborted) assessment of early DAP+CPT therapy versus standard monotherapy in MRSA bacteremia, hoping to encourage a more definitive clinical trial of its potential benefits against this leading cause of infection-associated mortality. (The clinical study discussed in this paper has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under identifier NCT02660346.).
Keywords: bacteremia; ceftaroline; daptomycin; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; mortality; vancomycin.
Copyright © 2019 Geriak et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline Associated with Better Clinical Outcomes than Standard of Care Monotherapy for Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia?Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Oct 22;63(11):e00900-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00900-19. Print 2019 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31640977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Kalil et al., "Is Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline Associated with Better Clinical Outcomes than Standard of Care Monotherapy for Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia?".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Oct 22;63(11):e01347-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01347-19. Print 2019 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31640978 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline the Way To Go for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia?Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Oct 22;63(11):e01725-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01725-19. Print 2019 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31640979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chang F-Y, Peacock JE, Musher DM, Triplett P, MacDonald BB, Mylotte JM, O’Donnell A, Wagener MM, Yu VL. 2003. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: recurrence and the impact of antibiotic treatment in a prospective multicenter study. Medicine 82:333–339. doi:10.1097/01.md.0000091184.93122.09. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical