Efficacy of Aminomethyl Spectinomycins against Complex Upper Respiratory Tract Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 30858215
- PMCID: PMC6496058
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02096-18
Efficacy of Aminomethyl Spectinomycins against Complex Upper Respiratory Tract Bacterial Infections
Abstract
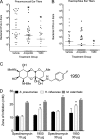
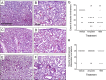
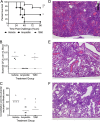
The most frequent ailment for which antibiotics are prescribed is otitis media (ear infections), which is most commonly caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae Treatment of otitis media is complicated by the fact that the bacteria in the middle ear typically form biofilms, which can be recalcitrant to antibiotic treatment. Furthermore, bacterial respiratory infections can be greatly exacerbated by viral coinfection, which is particularly evidenced by the synergy between influenza and S. pneumoniae In this study, we sought to ascertain the in vivo efficacy of aminomethyl spectinomycin lead 1950, an effective antibacterial agent both in vitro and in vivo against Streptococcus pneumoniae in the context of complex respiratory infections and acute otitis media. A single dose of 1950 significantly reduced bacterial burden in the respiratory tract for all three pathogens, even when species were present in a coinfection model. Additionally, a single dose of 1950 effectively reduced pneumococcal acute otitis media from the middle ear. The agent 1950 also proved efficacious in the context of influenza-pneumococcal super infection. These data further support the development of this family of compounds as potential therapeutic agents against the common causes of complex upper respiratory tract infections and acute otitis media.
Keywords: Haemophilus influenzae; Streptococcus pneumoniae; otitis media.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy with Chlorin e6 Is Bactericidal against Biofilms of the Primary Human Otopathogens.mSphere. 2020 Jul 15;5(4):e00492-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00492-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32669474 Free PMC article.
-
Otopathogens in the middle ear and nasopharynx of children with recurrent acute otitis media.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Jun;169:111552. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2023.111552. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37120991
-
Indirect pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis in polymicrobial otitis media occurs via interspecies quorum signaling.mBio. 2010 Jul 6;1(3):e00102-10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00102-10. mBio. 2010. PMID: 20802829 Free PMC article.
-
Otitis media pathogens - A life entrapped in biofilm communities.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019 Sep-Nov;45(5-6):595-612. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2019.1660616. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31502909 Review.
-
Recurrent and persistent otitis media.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000 Sep;19(9):911-6. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200009000-00034. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000. PMID: 11001126 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Relevance and Molecular Pathogenesis of the Emerging Serotypes 22F and 33F of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Spain.Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 27;11:309. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00309. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32174903 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antibacterial action of 3',6'-disubstituted spectinomycins.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024 Sep;77(9):577-588. doi: 10.1038/s41429-024-00750-2. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 38890386 Free PMC article.
-
Development of 2nd generation aminomethyl spectinomycins that overcome native efflux in Mycobacterium abscessus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 9;121(2):e2314101120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2314101120. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38165935 Free PMC article.
-
A Trivalent Live Vaccine Elicits Cross-Species Protection Against Acute Otitis Media in a Murine Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;12(12):1432. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121432. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772092 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cefuroxime axetil combined with Xingpi Yanger granules on the serum gastrin, motilin, and somatostatin levels in children with upper respiratory tract infection accompanied by diarrhea: results of a randomized trial.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Aug;10(8):2106-2113. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-314. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34584881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee RE, Hurdle JG, Liu J, Bruhn DF, Matt T, Scherman MS, Vaddady PK, Zheng Z, Qi J, Akbergenov R, Das S, Madhura DB, Rathi C, Trivedi A, Villellas C, Lee RB, Rakesh, Waidyarachchi SL, Sun D, McNeil MR, Ainsa JA, Boshoff HI, Gonzalez-Juarrero M, Meibohm B, Bottger EC, Lenaerts AJ. 2014. Spectinamides: a new class of semisynthetic antituberculosis agents that overcome native drug efflux. Nat Med 20:152–158. doi:10.1038/nm.3458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robertson GT, Scherman MS, Bruhn DF, Liu J, Hastings C, McNeil MR, Butler MM, Bowlin TL, Lee RB, Lee RE, Lenaerts AJ. 2017. Spectinamides are effective partner agents for the treatment of tuberculosis in multiple mouse infection models. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:770–777. doi:10.1093/jac/dkw467. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

