Benign biliary strictures: prevalence, impact, and management strategies
- PMID: 30858721
- PMCID: PMC6385742
- DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S165016
Benign biliary strictures: prevalence, impact, and management strategies
Abstract
Benign biliary strictures (BBSs) may form from chronic inflammatory pancreaticobiliary pathologies, postoperative bile-duct injury, or at biliary anastomoses following liver transplantation. Treatment aims to relieve symptoms of biliary obstruction, maintain long-term drainage, and preserve liver function. Endoscopic therapy, including stricture dilatation and stenting, is effective in most cases and the first-line treatment of BBS. Radiological and surgical therapies are reserved for patients whose strictures are refractory to endoscopic interventions. Response to treatment is dependent upon the technique and accessories used, as well as stricture etiology. In this review, we discuss the various BBS etiologies and their management strategies.
Keywords: benign biliary stricture; chronic pancreatitis; endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; liver transplantation; metal stent; plastic stent; primary sclerosing cholangitis; stricture dilatation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

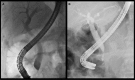
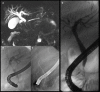
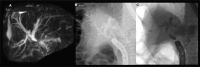
References
-
- Vitale GC, Tran TC, Davis BR, Vitale M, Vitale D, Larson G. Endoscopic management of postcholecystectomy bile duct strictures. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;206(5):918–923. discussion 924–925. - PubMed
-
- Gómez CM, Dumonceau JM, Marcolongo M, et al. Endoscopic management of biliary complications after adult living-donor versus deceased-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2009;88(11):1280–1285. - PubMed
-
- Chan CH, Donnellan F, Byrne MF, et al. Response to endoscopic therapy for biliary anastomotic strictures in deceased versus living donor liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2013;12(5):488–493. - PubMed
-
- Lévy P, Barthet M, Mollard BR, Amouretti M, Marion-Audibert AM, Dyard F. Estimation of the prevalence and incidence of chronic pancreatitis and its complications. Gastroentérol Clin Biol. 2006;30(6–7):838–844. - PubMed
-
- Wang LW, Li ZS, Li SD, Jin ZD, Zou DW, Chen F. Prevalence and clinical features of chronic pancreatitis in China: a retrospective multicenter analysis over 10 years. Pancreas. 2009;38(3):248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

