Vildagliptin Reduces Stenosis of Injured Carotid Artery in Diabetic Mouse Through Inhibiting Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation via ER Stress/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 30858802
- PMCID: PMC6397934
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00142
Vildagliptin Reduces Stenosis of Injured Carotid Artery in Diabetic Mouse Through Inhibiting Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation via ER Stress/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
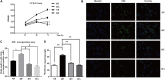
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors are novel anti-hyperglycemic drugs for type 2 diabetes. It has been reported that DDP-4 inhibitor could exert pleiotropic effects on cardiovascular system. This study was to explore the effect and mechanism of vildagliptin on the stenosis of injured carotid artery in diabetic mouse. Twenty six-week-old male db/db mice (BKS) were randomized into vildagliptin treated and vehicle control groups. Ligation injury was first performed in left carotid arteries of all diabetic mice, then oral vildagliptin or equal amount of PBS was correspondingly administered to the mice from the next day to ligation injury for 4 weeks. Effects on proliferation were detected via histological and morphometric analysis. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) markers were determined by immunoblot analysis. After 4 weeks of vildagliptin delivery, it was observed that the intimal area and neointimal thickness of the ligated carotid arteries were significantly reduced as compared to the control group. In vivo, vildagliptin suppressed the expressions of PCNA and α-SMA, phospho-p65, phospho-IKKα/β, GRP78 and CHOP, as well as IRE-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). In vitro, the proliferation and hypertrophy of VSMCs were significantly inhibited by blocking the IRE-1 pathway, and the inhibition of phospho-IRE-1 expression down-regulated the expression of phospho-IKKα/β in VSMCs. Vildagliptin reduced the stenosis of injured carotid arteries in diabetic mice, and this effect was achieved via inhibiting the activation of ER stress/NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: VSMCs proliferation; phospho-IKKα/β; phospho-IRE-1; phospho-p65; vildagliptin.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, vildagliptin, inhibits pancreatic beta cell apoptosis in association with its effects suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in db/db mice.Metabolism. 2015 Feb;64(2):226-35. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Metabolism. 2015. PMID: 25195070
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition by gemigliptin prevents abnormal vascular remodeling via NF-E2-related factor 2 activation.Vascul Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;73:11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26187356
-
Osthole inhibits intimal hyperplasia by regulating the NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad2 signalling pathways in the rat carotid artery after balloon injury.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;811:232-239. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.06.025. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28648404
-
Favorable effects of vildagliptin on metabolic and cognitive dysfunctions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 15;769:297-305. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.11.033. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26607467
-
Vasculoprotective Effects of Vildagliptin. Focus on Atherogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 25;21(7):2275. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072275. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32218354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Insight into the Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Pathogenesis of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Mar 26;2021:5529810. doi: 10.1155/2021/5529810. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33854692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular protection by DPP-4 inhibitors in preclinical studies: an updated review of molecular mechanisms.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;395(11):1357-1372. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02279-3. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35945358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and Vascular Diseases: A Focused Review on Smooth Muscle Cell Function.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 8;11:635. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00635. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32457625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of IRE1α in vascular diseases.J Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Nov 10;18(4):e12056. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.12056. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39691875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incretins-Based Therapies and Their Cardiovascular Effects: New Game-Changers for the Management of Patients with Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 1;15(7):1858. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071858. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen J., Zhang M., Zhu M., Gu J., Song J., Cui L., et al. (2018). Paeoniflorin prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells via the IRE1alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Food Funct. 9 2386–2397. 10.1039/c7fo01406f - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

