Licochalcone A Protects the Blood-Milk Barrier Integrity and Relieves the Inflammatory Response in LPS-Induced Mastitis
- PMID: 30858849
- PMCID: PMC6398509
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00287
Licochalcone A Protects the Blood-Milk Barrier Integrity and Relieves the Inflammatory Response in LPS-Induced Mastitis
Abstract
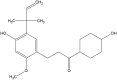
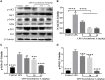
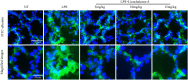
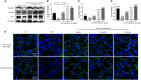
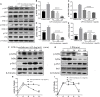
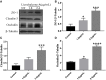
Background/Aims: Mastitis is an acute clinical inflammatory response. The occurrence and development of mastitis seriously disturb women's physical and mental health. Licochalcone A, a phenolic compound in Glycyrrhiza uralensis, has anti-inflammatory properties. Here, we examined the effect of licochalcone A on blood-milk barrier and inflammatory response in LPS-induced mice mastitis. Methods:In vivo, we firstly established mice models of mastitis by canal injection of LPS to mammary gland, and then detected the effect of licochalcone A on pathological indexes, inflammatory responses and blood-milk barrier in this model. In vivo, Mouse mammary epithelial cells (mMECs) were treated with licochalcone A prior to the incubation of LPS, and then the inflammatory responses, tight junction which is the basic structure of blood-milk barrier were analyzed. Last, we elucidated the anti-inflammatory mechanism by examining the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and AKT/NF-κB signaling pathways in vivo and in vitro. Result: The in vivo results showed that licochalcone A significantly decreased the histopathological impairment and the inflammatory responses, and improved integrity of blood-milk barrier. The in vitro results demonstrated that licochalcone A inhibited LPS-induced inflammatory responses and increase the protein levels of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin3 in mMECs. The in vivo and in vitro mechanistic study found that the anti-inflammatory effect of licochalcone A in LPS-induced mice mastitis was mediated by MAPK and AKT/NF-κB signaling pathways. Conclusions and Implications: Our experiments collectively indicate that licochalcone A protected against LPS-induced mice mastitis via improving the blood-milk barrier integrity and inhibits the inflammatory response by MAPK and AKT/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Keywords: AKT/NF-κB; MAPK; blood–milk barrier; licochalcone A; mMECs; mastitis.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Morin alleviates LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT, MAPK, NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathway and protecting the integrity of blood-milk barrier.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:105972. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105972. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31711938
-
Formononetin Protects LPS-Induced Mastitis Through Suppressing Inflammation and Enhancing Blood-Milk Barrier Integrity via AhR-Induced Src Inactivation.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 3;13:814319. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.814319. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35185907 Free PMC article.
-
Farrerol Relieve Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Mastitis by Inhibiting AKT/NF-κB p65, ERK1/2 and P38 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 14;19(6):1770. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061770. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29904013 Free PMC article.
-
Invited review: The role of the blood-milk barrier and its manipulation for the efficacy of the mammary immune response and milk production.J Dairy Sci. 2021 Jun;104(6):6376-6388. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-20029. Epub 2021 Mar 25. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 33773785 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential and action mechanisms of licochalcone B: a mini review.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jul 3;11:1440132. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1440132. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39021879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Licochalcone a Induces ROS-Mediated Apoptosis through TrxR1 Inactivation in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 27;2020:5875074. doi: 10.1155/2020/5875074. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596335 Free PMC article.
-
Licochalcone A activation of glycolysis pathway has an anti-aging effect on human adipose stem cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Dec 3;13(23):25180-25194. doi: 10.18632/aging.203734. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34862330 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Licochalcone A via Regulation of ORAI1 and K+ Channels in T-Lymphocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 7;22(19):10847. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910847. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639190 Free PMC article.
-
Tartary buckwheat flavonoids relieve the tendency of mammary fibrosis induced by HFD during pregnancy and lactation.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Dec 10;13(23):25377-25392. doi: 10.18632/aging.203752. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34890369 Free PMC article.
-
Evodiamine Relieve LPS-Induced Mastitis by Inhibiting AKT/NF-κB p65 and MAPK Signaling Pathways.Inflammation. 2022 Feb;45(1):129-142. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01533-9. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 34401976
References
-
- Meretoja T, Ihalainen H, Leidenius M. Inflammations of the mammary gland. Duodecim (2017) 133:855–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

