Progress in EBV Vaccines
- PMID: 30859093
- PMCID: PMC6398348
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00104
Progress in EBV Vaccines
Abstract
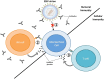
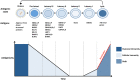
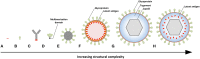
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous pathogen that imparts a significant burden of disease on the human population. EBV is the primary cause of infectious mononucleosis and is etiologically linked to the development of numerous malignancies. In recent years, evidence has also been amassed that strongly implicate EBV in the development of several autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis. Prophylactic and therapeutic vaccination has been touted as a possible means of preventing EBV infection and controlling EBV-associated diseases. However, despite several decades of research, no licensed EBV vaccine is available. The majority of EBV vaccination studies over the last two decades have focused on the major envelope protein gp350, culminating in a phase II clinical trial that showed soluble gp350 reduced the incidence of IM, although it was unable to protect against EBV infection. Recently, novel vaccine candidates with increased structural complexity and antigenic content have been developed. The ability of next generation vaccines to safeguard against B-cell and epithelial cell infection, as well as to target infected cells during all phases of infection, is likely to decrease the negative impact of EBV infection on the human population.
Keywords: EBV (Epstein-Barr virus); lympho proliferative disorder; oncogenic; vaccine; γ-herpesvirus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein Barr Virus: Development of Vaccines and Immune Cell Therapy for EBV-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:734471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.734471. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prophylactic and Therapeutic EBV Vaccines: Major Scientific Obstacles, Historical Progress, and Future Direction.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 7;9(11):1290. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111290. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-barr virus vaccines.Clin Transl Immunology. 2015 Jan 23;4(1):e32. doi: 10.1038/cti.2014.27. eCollection 2015 Jan. Clin Transl Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25671130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential for EBV Vaccines to Prevent Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 24;13:887794. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.887794. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35812097 Free PMC article.
-
Rabbits immunized with Epstein-Barr virus gH/gL or gB recombinant proteins elicit higher serum virus neutralizing activity than gp350.Vaccine. 2016 Jul 25;34(34):4050-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.06.021. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27291087
Cited by
-
CAR-T Cells Targeting Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 Validated in a Humanized Mouse Model of EBV Infection and Lymphoproliferative Disease.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Aug 8;18:504-524. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.08.005. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32953984 Free PMC article.
-
Urgency and necessity of Epstein-Barr virus prophylactic vaccines.NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Dec 9;7(1):159. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00587-6. NPJ Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 36494369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the gut and tumor microbiota in cancer.Nat Med. 2022 Apr;28(4):690-703. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01779-2. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35440726 Review.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus as a genetic disease.Clin Immunol. 2022 Mar;236:108953. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.108953. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35149194 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Immunotherapy to Overcome Resistance in Viral-Associated Head and Neck Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 16;11:649963. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.649963. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34336649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Longnecker L, Kieff E, Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr Virus Phiadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; (2013).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

