Multi-Functional Drug Carrier Micelles With Anti-inflammatory Drug
- PMID: 30859098
- PMCID: PMC6397834
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00093
Multi-Functional Drug Carrier Micelles With Anti-inflammatory Drug
Abstract
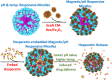
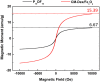
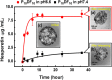
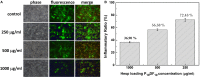
The multi-functional micelles poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-10 undecanoic acid)/CM-Dextran Fe3O4 (PNDU/CM-Dex Fe3O4) were poly (NIPAAm-co-DMAAm-co-UA) (PNDU) grafting hydrophilic CM-Dextran Fe3O4 which possess pH-dependent temperature response and magnetic response. In this research, anti-inflammation drug Hesperetin was encapsulated by micelles using membrane dialysis method to obtain the different ratio of Hesperetin-embedded P5DF10, P10DF10, and P20DF10. These micelles were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, 1H-NMR, thermogravimetric analyzer, and superconducting quantum interference device magnetometer. The morphology and particle size of micelles was observed by transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. The low critical solution temperature of the P10DF10 micelles is in pH 6.6 at about 37.76°C and in pH 7.4 at about 41.70°C. The biocompatibility of micelles was confirmed by cytotoxicity study. Inflammatory inhibition of hesperetin-embedded P10DF10 micelles also studied through RAW264.7. Hesperetin-embed P10DF10 micelles suppressed LPS-induced inflammatory response. Via immunofluorescence cell staining demonstrate that Hesperetin-embed P10DF10 micelles inhibited the activation of NF-κB p60 and markedly attenuated in a drug dose-dependent manner. At a concentration of 1,000 ug/ml, an inflammatory rate can be reduced to 36.9%. Based on these results, the hesperetin-embed P10DF10 micelles had successfully synthesized and enable to carry and release the anti-inflammatory drugs, which instrumental for biomedical therapy and applications.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory drug; drug carrier; magnetic micelles; pH response micelles; temperature response micelles.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Preparation and characterization of biocompatible and thermoresponsive micelles based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide) grafted on polysuccinimide for drug delivery.J Biomater Appl. 2014 Sep;29(3):442-53. doi: 10.1177/0885328214533736. Epub 2014 May 12. J Biomater Appl. 2014. PMID: 24825758
-
Thermo-responsive release of curcumin from micelles prepared by self-assembly of amphiphilic P(NIPAAm-co-DMAAm)-b-PLLA-b-P(NIPAAm-co-DMAAm) triblock copolymers.Int J Pharm. 2014 Dec 10;476(1-2):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.09.029. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Int J Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25260217
-
Incorporation and in vitro release of doxorubicin in thermally sensitive micelles made from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide)-b-poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) with varying compositions.Biomaterials. 2005 Aug;26(24):5064-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.01.030. Biomaterials. 2005. PMID: 15769542
-
Thermally sensitive micelles self-assembled from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide)-b-poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) for controlled delivery of paclitaxel.Mol Biosyst. 2005 Jul;1(2):158-65. doi: 10.1039/b501756b. Epub 2005 Jun 9. Mol Biosyst. 2005. PMID: 16880979
-
Novel stimuli-responsive micelle self-assembled from Y-shaped P(UA-Y-NIPAAm) copolymer for drug delivery.Biomacromolecules. 2006 Nov;7(11):2956-60. doi: 10.1021/bm060080k. Biomacromolecules. 2006. PMID: 17096519
Cited by
-
Magnetic Micellar Nanovehicles: Prospects of Multifunctional Hybrid Systems for Precision Theranostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 4;23(19):11793. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911793. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Microfluidic Chip System with Giant Magnetoresistance Sensor for High-Sensitivity Detection of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;13(8):807. doi: 10.3390/bios13080807. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622894 Free PMC article.
-
Key Points in Remote-Controlled Drug Delivery: From the Carrier Design to Clinical Trials.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9149. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179149. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased antitumor efficacy of ginsenoside Rh2 via mixed micelles: in vivo and in vitro evaluation.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):1369-1377. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1825542. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32998576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bok S. H., Lee S. H., Park Y. B., Bae K. H., Son K. H., Jeong T. S., et al. . (1999). Plasma and hepatic cholesterol and hepatic activities of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase and acyl CoA: cholesterol transferase are lower in rats fed citrus peel extract or a mixture of citrus bioflavonoids. J. Nutr. 129, 1182–1185. 10.1093/jn/129.6.1182 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cline M. J. (1970). Leukocyte function in inflammation: the ingestion, killing, and digestion of microorganisms. Ser. Haematol. 3, 3–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

