Circulating Extracellular Vesicles and Their miR "Barcode" Differentiate Alcohol Drinkers With Liver Injury and Those Without Liver Injury in Severe Trauma Patients
- PMID: 30859103
- PMCID: PMC6397866
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00030
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles and Their miR "Barcode" Differentiate Alcohol Drinkers With Liver Injury and Those Without Liver Injury in Severe Trauma Patients
Abstract
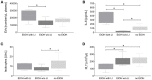
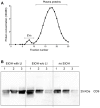
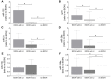
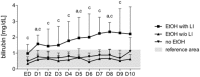
Short Summary: Extracellular vesicles (EVs), released during tissue/cell injury, contain a "barcode" indicating specific microRNAs (miRs) that can uncover their origin. We examined whether systemic EVs possessing hepatic miR-signatures would indicate ongoing liver injury and clinical complications in trauma patients (TP). We grouped the patients of alcoholic drinkers into "alcohol-drinkers with liver injury (LI)" (EtOH with LI) or "alcohol-drinkers without LI" (EtOH w/o LI) and we compared these groups to "non-drinkers" (no EtOH). When we examined patient blood from the EtOH with LI group we found the total number of EVs to be increased, along with an increase in miR-122 and let7f-two EV-associated miRNAs-and several inflammation-associating cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-33. In contrast, all of the aforementioned readouts were found to be decreased in the EtOH w/o LI group. These novel data demonstrate that hepatocyte damage in alcohol-intoxicated trauma patients presenting with liver injury can be reflected by an increase in circulating serum EVs, their specific miR-"barcode" and the concomitant increase of systemic inflammatory markers IL-6 and IL-33. Anti-inflammatory effect of alcohol-drinking in EtOH w/o LI can be presented by a reduced number of hepato-derived EVs, no upregulation of IL-6 and IL-33, and a miR "barcode" different from patients presenting with liver injury. Background: Alcohol abuse is associated with (neuro)protective effects related to (head) injuries, and with negative effects regarding infection rates and survival in severely injured trauma patients (TP). Extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are released during tissue and/or cell injury, can contain a "barcode" including specific microRNAs (miRs) that uncover their origin. We examined whether EVs with a hepatic miR signature can be systemically measured, and whether they can indicate ongoing liver injury in alcohol-intoxicated TP and foretell clinical complications. Patients/Methods: We enrolled 35 TP and measured blood EVs, IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-10 and IL-33, alcohol (ethanol, EtOH) concentration (BAC), GLDH, GGT, AST, ALT, leukocytes, platelets, and bilirubin. Within circulating EVs we measured the expression levels of miR-122, let7f, miR21, miR29a, miR-155, and miR-146a. Patients of alcohol-drinkers were grouped into "alcohol drinkers with liver injury (LI)" (EtOH with LI) or "alcohol drinkers without LI" (EtOH w/o LI) and compared to "non-drinkers" (no EtOH). We assessed systemic injury characteristics and the outcome of hospitalization with regard to sepsis, septic shock, pneumonia, or mortality. Results: EtOH with LI patients had significantly increased rates of pneumonia vs. the EtOH w/o LI group. EVs, IL-6, and IL-33 levels were significantly increased in EtOH with LI vs. EtOH w/o LI group (p < 0.05). EV number correlated positively with ALT and IL-6 (p < 0.0001). Two miRs, miR-122 and let7f, were increased only in the blood EVs from the EtOH with LI group (p < 0.05). Five miRs, miR-122, let7f, miR-21, miR-29a, and miR-146a, were reduced in the blood EVs from the EtOH w/o LI group, vs. no EtOH (p < 0.05). Notably miR-122 correlated significantly with increased bilirubin levels in the EtOH with LI group (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Liver injury in alcohol-intoxicated TP is reflected by increased EV numbers, their specific miR barcode, and the correlated increase of systemic inflammatory markers IL-6 and IL-33. Interestingly, severely injured TP without liver injury were found to have a reduced number of liver-derived EVs, no observed inflammatory infiltration and reduced specific miR "barcode."
Keywords: alcohol; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; miR; outcome; trauma.
Figures
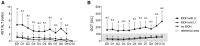

Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles released by hepatocytes from gastric infusion model of alcoholic liver disease contain a MicroRNA barcode that can be detected in blood.Hepatology. 2017 Feb;65(2):475-490. doi: 10.1002/hep.28838. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 27639178 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of positive blood alcohol concentration on outcome and systemic interleukin-6 in major trauma patients.Injury. 2016 Mar;47(3):640-5. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.01.016. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Injury. 2016. PMID: 26850862
-
Circulating Plasma Extracellular Vesicles from Septic Mice Induce Inflammation via MicroRNA- and TLR7-Dependent Mechanisms.J Immunol. 2018 Dec 1;201(11):3392-3400. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801008. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30355788 Free PMC article.
-
Immunothrombotic Activity of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Extracellular Vesicles in Secondary Organ Failure Induced by Trauma and Sterile Insults.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 8;9:190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00190. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29472928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating extracellular vesicles as a potential source of new biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Mar 21;225(3):401-6. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24462978 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Acute or Chronic Alcohol Intake on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 10;21(24):9407. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249407. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33321885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
let7f‑5p attenuates inflammatory injury in in vitro pneumonia models by targeting MAPK6.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Feb;23(2):95. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11734. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33300070 Free PMC article.
-
Small extracellular vesicles and liver diseases: From diagnosis to therapy.World J Hepatol. 2022 Jul 27;14(7):1307-1318. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1307. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36158910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns in trauma.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020 Aug;46(4):751-775. doi: 10.1007/s00068-019-01235-w. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020. PMID: 31612270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Substance Abuse and HIV-Related Neurological Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 15;21(18):6765. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186765. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32942668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

