Glaucoma Diagnosis: from the Artisanal to the Defined
- PMID: 30859172
- PMCID: PMC6407894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ogla.2018.06.002
Glaucoma Diagnosis: from the Artisanal to the Defined
Abstract
In 400BC, Hippocrates wrote the first record of glaucoma. Since then, increasingly objective diagnostic techniques have enabled earlier detection of glaucoma and its progression, providing greater certainty in decision-making and early medical and surgical intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Dr. Schuman receives royalties for intellectual property licensed by Massachusetts Eye and Ear and Massachusetts Institute of Technology to Zeiss.
Figures



Similar articles
-
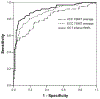
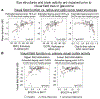
Structural glaucomatous damage vs. visual field defects: longitudinal study in patients with ocular hypertension or early primary open-angle glaucoma.Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 2002;236:45-6. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0420.80.s236.26.x. Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12390135 No abstract available.
-
Assessment of glaucoma imaging technology.Ophthalmology. 2008 Jul;115(7):1266-7; author reply 1267-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.02.003. Ophthalmology. 2008. PMID: 18598824 No abstract available.
-
Mapping the visual field.Ophthalmology. 2001 Oct;108(10):1714. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(01)00733-3. Ophthalmology. 2001. PMID: 11581028 No abstract available.
-
Correlating Structural and Functional Damage in Glaucoma.J Glaucoma. 2019 Dec;28(12):1079-1085. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001346. J Glaucoma. 2019. PMID: 31478953 Review.
-
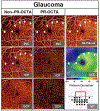
[The ophthalmoscopic characteristics of the optic disk and the retinal layer of nerve fibers of the retina in glaucoma].Vestn Oftalmol. 2005 Jul-Aug;121(4):46-9. Vestn Oftalmol. 2005. PMID: 16223048 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Literature Review on Artificial Intelligence Methods for Glaucoma Screening, Segmentation, and Classification.J Imaging. 2022 Jan 20;8(2):19. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8020019. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35200722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Glaucoma: Advances in Diagnosis, Progression Forecasting, and Surgical Outcome Prediction.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 8;26(10):4473. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104473. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hippocrates. Aphorisms. III. 31.6: The Internet Classic Archives; Translated by Adams Francis. classics.mit.edu/Hippocrates/aphorisms.html
-
- Aristotle. De Generatuibe Animalium. Translated by Peck AL 1970 Internet Archive Cambridge Harvard University Press; archive.org/details/generationofanim00arisuoft
-
- Galen. Ars Medica. Edited and translated by Ian Johnston. Loeb Classical Library; www.loebclassics.com/view/galen-art_medicine/2016/pb_LCL523.139.xml.
-
- Marjanovic I. The History of Detecting Glaucomatous Changes in the Optic Disc Glaucoma- Basic and Clinical Aspects. Belgrade, Serbia: a: Intech; p. chapter 13 (289).
-
- Mackenzie W Practical treatise on the Diseases of the Eye. London: Longman, Orme, Brown, Green and Longmans; 1830.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
