Intraoperative multispectral and hyperspectral label-free imaging: A systematic review of in vivo clinical studies
- PMID: 30859757
- PMCID: PMC6736677
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201800455
Intraoperative multispectral and hyperspectral label-free imaging: A systematic review of in vivo clinical studies
Abstract
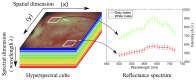
Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging (HSI) are emerging optical imaging techniques with the potential to transform the way surgery is performed but it is not clear whether current systems are capable of delivering real-time tissue characterization and surgical guidance. We conducted a systematic review of surgical in vivo label-free multispectral and HSI systems that have been assessed intraoperatively in adult patients, published over a 10-year period to May 2018. We analysed 14 studies including 8 different HSI systems. Current in-vivo HSI systems generate an intraoperative tissue oxygenation map or enable tumour detection. Intraoperative tissue oxygenation measurements may help to predict those patients at risk of postoperative complications and in-vivo intraoperative tissue characterization may be performed with high specificity and sensitivity. All systems utilized a line-scanning or wavelength-scanning method but the spectral range and number of spectral bands employed varied significantly between studies and according to the system's clinical aim. The time to acquire a hyperspectral cube dataset ranged between 5 and 30 seconds. No safety concerns were reported in any studies. A small number of studies have demonstrated the capabilities of intraoperative in-vivo label-free HSI but further work is needed to fully integrate it into the current surgical workflow.
Keywords: hyperspectral imaging; multispectral imaging; surgery.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Biophotonics published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
-
- JA C, EC W, Chin JA, Wang EC, Kibbe MR. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:1679–1688. - PubMed
-
- Chiang N, Jain JK, Sleigh J, Vasudevan T. J Vasc Surg. 2017;66:1192. - PubMed
-
- Nourrit V, Denniss J, Muqit MMK, Schiessl I, Fenerty C, Stanga PE, Henson DB. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2010;33:686. - PubMed
-
- Desjardins M, Sylvestre JP, Jafari R, Kulasekara S, Rose K, Trussart R, Arbour JD, Hudson C, Lesage F. Exp Eye Res. 2016;146:330. - PubMed
-
- Greenman RL, Panasyuk S, Wang X, Lyons TE, Dinh T, Longoria L, Giurini JM, Freeman J, Khaodhiar L, Veves A. Lancet. 2005;366:1711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

