Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review
- PMID: 30861319
- PMCID: PMC6973275
- DOI: 10.1002/jrsm.1346
Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review
Abstract
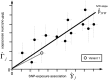
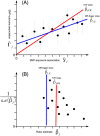
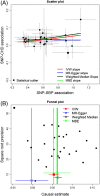
Mendelian randomization (MR) uses genetic variants as instrumental variables to infer whether a risk factor causally affects a health outcome. Meta-analysis has been used historically in MR to combine results from separate epidemiological studies, with each study using a small but select group of genetic variants. In recent years, it has been used to combine genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data for large numbers of genetic variants. Heterogeneity among the causal estimates obtained from multiple genetic variants points to a possible violation of the necessary instrumental variable assumptions. In this article, we provide a basic introduction to MR and the instrumental variable theory that it relies upon. We then describe how random effects models, meta-regression, and robust regression are being used to test and adjust for heterogeneity in order to improve the rigor of the MR approach.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; meta-analysis; pleiotropy; two-sample summary data MR.
© 2019 The Authors Research Synthesis Methods Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reported no conflict of interest.
Figures
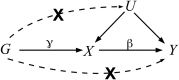

References
-
- Davey Smith G, Ebrahim S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int J Epidemiol. 2003;32(1):1‐22. - PubMed
-
- Pearl J. Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference. New York, NY, USA: 2nd edn: Cambridge University Press; 2009.
-
- Vansteelandt S, Bowden J, Babanezhad M, Goetghebeur E. On instrumental variables estimation of causal odds ratios. Statistical Science. 2011;26(3):403‐422.
-
- Zhao Q, Wang J, Hemani G, Bowden J, Small D. Statistical inference in two‐sample summary‐data Mendelian randomization using robust adjusted profile score. ArXiv 2018. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.09652.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

