The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 30862074
- PMCID: PMC6468751
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9030096
The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
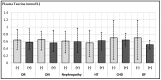
Background: Taurine has an active role in providing glucose homeostasis and diabetes causes a decline in taurine levels. This paper investigates the relationship between taurine and diabetic complications, patients' demographic features, and biochemical parameters. Methods: Fifty-nine patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and 28 healthy control subjects between the ages of 32 and 82 were included in the study. The mean age of subjects was 55.6 ± 10.3 and mean diabetes duration was 10.2 ± 6.0 years. The most commonly accompanying comorbidity was hypertension (HT) (64.5%, n = 38), and the most frequent diabetic complication was neuropathy (50.8%, n = 30). Plasma taurine concentrations were measured by an enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) kit. Results: Plasma taurine concentrations were significantly lower in diabetic patients (0.6 ± 0.1 mmol/L) than controls (0.8 ± 0.2 mmol/L) and in hypertensive (0. 6 ± 0.1 mmol/L) patients (p = 0.000, p = 0.027 respectively). Conclusion: Plasma taurine levels were decreased in patients with T2DM and this was not related to FBG, HbA1c, and microalbuminuria. With regard to complications, we only found a correlation with neuropathy. We suggest that taurine levels may be more important in the development of diabetes; however, it may also have importance for the progression of the disease and the subsequent complications. We further assert that taurine measurement at different times may highlight whether there is a causal relationship in the development of complications.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic neuropathy; diabetic retinopathy; microalbuminuria; taurine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016: Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:S13–S22. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global report on diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- TURDEP-II Study Group Diabetes epidemic in Turkey: results of the second population-based survey of diabetes and risk characteristics in Turkey (TURDEP-II) Diabetologia. 2011;54:140.
-
- Powers A.C. Diabetes mellitus. In: Fauci A.S., Hauser S., Longo D., Jameson J.L., Loscalzo J., editors. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, Kasper, D.L. McGraw Hill Education; New York, NY, USA: 2015.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical