Remote Monitoring of Diabetes: A Cloud-Connected Digital System for Individuals With Diabetes and Their Health Care Providers
- PMID: 30862245
- PMCID: PMC6835183
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296819834054
Remote Monitoring of Diabetes: A Cloud-Connected Digital System for Individuals With Diabetes and Their Health Care Providers
Abstract
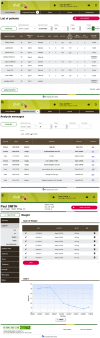
Benefits of telemedicine have been proven in the field of diabetes. Among a number of technical solutions, Diabeo® has been studied in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes with intensive insulin therapy. This digital therapeutic system contains a self-monitoring glucose logbook and offers automated insulin dose recommendations thanks to a fully customizable algorithm. In addition, the cloud-based dedicated software also has features to facilitate remote monitoring, including a platform for diabetes nurses who perform coaching and treatment adjustment. A detailed description of this telemedicine system is provided, as well as results of completed clinical studies. In particular, TeleDiab 1's positive results on HbA1c in type 1 diabetes are detailed. We conclude with a discussion of the role of this telemedicine system within the landscape of mobile apps for diabetes.
Keywords: insulin therapy; remote monitoring; telemedicine; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Dalal MR, Grabner M, Bonine N, Stephenson JJ, DiGenio A, Bieszk N. Are patients on basal insulin attaining glycemic targets? Characteristics and goal achievement of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with basal insulin and physician-perceived barriers to achieving glycemic targets. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;121:17-26. - PubMed
-
- Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, et al. ; T1D Exchange Clinic Network. Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:971-978. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier G, Benhamou PY, Dardari D, et al. ; TeleDiab Study Group. The Diabeo software enabling individualized insulin dose adjustments combined with telemedicine support improves HbA1c in poorly controlled type 1 diabetic patients: a 6-month, randomized, open-label, parallel-group, multicenter trial (TeleDiab 1 Study). Diabetes Care. 2011;34:533-539. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

