Selective laser trabeculoplasty versus eye drops for first-line treatment of ocular hypertension and glaucoma (LiGHT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 30862377
- PMCID: PMC6495367
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32213-X
Selective laser trabeculoplasty versus eye drops for first-line treatment of ocular hypertension and glaucoma (LiGHT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2019 Jul 6;394(10192):e1. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31503-X. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31282363 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension are habitually treated with eye drops that lower intraocular pressure. Selective laser trabeculoplasty is a safe alternative but is rarely used as first-line treatment. We compared the two.
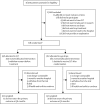
Methods: In this observer-masked, randomised controlled trial treatment-naive patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension and no ocular comorbidities were recruited between 2012 and 2014 at six UK hospitals. They were randomly allocated (web-based randomisation) to initial selective laser trabeculoplasty or to eye drops. An objective target intraocular pressure was set according to glaucoma severity. The primary outcome was health-related quality of life (HRQoL) at 3 years (assessed by EQ-5D). Secondary outcomes were cost and cost-effectiveness, disease-specific HRQoL, clinical effectiveness, and safety. Analysis was by intention to treat. This study is registered at controlled-trials.com (ISRCTN32038223).
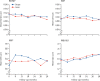
Findings: Of 718 patients enrolled, 356 were randomised to the selective laser trabeculoplasty and 362 to the eye drops group. 652 (91%) returned the primary outcome questionnaire at 36 months. Average EQ-5D score was 0·89 (SD 0·18) in the selective laser trabeculoplasty group versus 0·90 (SD 0·16) in the eye drops group, with no significant difference (difference 0·01, 95% CI -0·01 to 0·03; p=0·23). At 36 months, 74·2% (95% CI 69·3-78·6) of patients in the selective laser trabeculoplasty group required no drops to maintain intraocular pressure at target. Eyes of patients in the selective laser trabeculoplasty group were within target intracoluar pressure at more visits (93·0%) than in the eye drops group (91·3%), with glaucoma surgery to lower intraocular pressure required in none versus 11 patients. Over 36 months, from an ophthalmology cost perspective, there was a 97% probability of selective laser trabeculoplasty as first treatment being more cost-effective than eye drops first at a willingness to pay of £20 000 per quality-adjusted life-year gained.
Interpretation: Selective laser trabeculoplasty should be offered as a first-line treatment for open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension, supporting a change in clinical practice.
Funding: National Institute for Health Research, Health and Technology Assessment Programme.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Laser trabeculoplasty as first-line glaucoma treatment.Lancet. 2019 Apr 13;393(10180):1479-1480. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32553-4. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 30862378 No abstract available.
-
Laser treatment for glaucoma.Lancet. 2020 Sep 12;396(10253):754. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31059-X. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32919505 No abstract available.
References
-
- Haymes SA, Leblanc RP, Nicolela MT, Chiasson LA, Chauhan BC. Risk of falls and motor vehicle collisions in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:1149–1155. - PubMed
-
- Haymes SA, LeBlanc RP, Nicolela MT, Chiasson LA, Chauhan BC. Glaucoma and on-road driving performance. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008;49:3035–3041. - PubMed
-
- Garway-Heath DF, Crabb DP, Bunce C. Latanoprost for open-angle glaucoma (UKGTS): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;385:1295–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

