Genome-Wide RNAi Screen Identifies PMPCB as a Therapeutic Vulnerability in EpCAM+ Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 30862714
- PMCID: PMC6497533
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3015
Genome-Wide RNAi Screen Identifies PMPCB as a Therapeutic Vulnerability in EpCAM+ Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
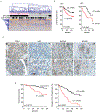
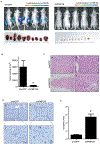
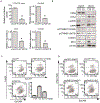
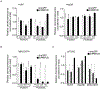
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a genetically heterogeneous disease for which a dominant actionable molecular driver has not been identified. Patients with the stem cell-like EpCAM+AFP+ HCC subtype have poor prognosis. Here, we performed a genome-wide RNAi screen to identify genes with a synthetic lethal interaction with EpCAM as a potential therapeutic target for the EpCAM+AFP+ HCC subtype. We identified 26 candidate genes linked to EpCAM/Wnt/β-catenin signaling and HCC cell growth. We further characterized the top candidate PMPCB, which plays a role in mitochondrial protein processing, as a bona fide target for EpCAM+ HCC. PMPCB blockage suppressed EpCAM expression and Wnt/β-catenin signaling via mitochondria-related reactive oxygen species production and FOXO activities, resulting in apoptosis and tumor suppression. These results indicate that a synthetic lethality screen is a viable strategy to identify actionable drivers of HCC and identify PMPCB as a therapeutically vulnerable gene in EpCAM+ HCC subpopulations. SIGNIFICANCE: This study identifies PMPCB as critical to mitochondrial homeostasis and a synthetic lethal candidate that selectively kills highly resistant EpCAM+ HCC tumors by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

