Focus Tracking System for Femtosecond Laser Machining using Low Coherence Interferometry
- PMID: 30862829
- PMCID: PMC6414527
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40749-6
Focus Tracking System for Femtosecond Laser Machining using Low Coherence Interferometry
Abstract
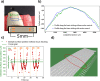
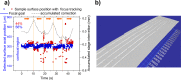
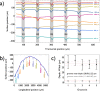
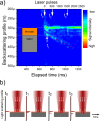
We designed a real time, single-laser focus tracking system using low coherence properties of the machining femtosecond laser itself in order to monitor and correct the sample position relative to the focal plane. Using a Michelson Interferometer, the system collects data arising from part of the beam backscattered at the ablation spot. The data is analyzed by a custom software for position correction (employing an XYZ automated translation stage). With the focus tracking enabled we were able to etch channels with a stable cross-section profile on a bovine tooth with relief amplitude tens of times greater than the Rayleigh length of the system, keeping the sample inside the confocal parameter during most of the processing time. Moreover, the system is also capable of monitoring crater depth evolution during the ablation process, allowing for material removal assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sugioka, K. & Cheng, Y. Ultrafast lasers-reliable tools for advanced materials processing. Light-Sci. Appl. 3 (2014).
-
- Samad, R. E., Machado, L. M., Vieira Junior, N. D. & de Rossi, W. In Laser pulses - theory, technology, and applications (ed. Prof. Igor Peshko) (InTech, 2012).
-
- Cao BX, et al. Real-time laser focusing system for high-precision micromachining using diffractive beam sampler and advanced image sensor. Opt. and Las. in Eng. 2018;107:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.03.002. - DOI
-
- Deck, L. & Degroot, P. High-speed noncontact profiler based on scanning white-light interferometry. Appl. Opt. 33 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

