Histamine H3 receptor antagonist E177 attenuates amnesia induced by dizocilpine without modulation of anxiety-like behaviors in rats
- PMID: 30863075
- PMCID: PMC6388968
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S193125
Histamine H3 receptor antagonist E177 attenuates amnesia induced by dizocilpine without modulation of anxiety-like behaviors in rats
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer disease (AD) is the main cause of dementia in elderly people. The potential of histamine H3 receptor (H3R) antagonists as a pharmacological treatment of several neuropsychiatric diseases is well established.
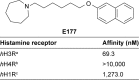
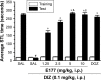
Methods: The novel non-imidazole-based H3R antagonist E177 was screened for its pro-cognitive effects on the inhibitory avoidance paradigm (IAP) and novel object recognition (NOR) task in a dizocilpine (DIZ)-induced model of amnesia in male Wistar rats. Donepezil, an acetylcholine esterase inhibitor, was used as the reference drug.
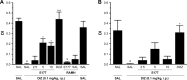
Results: Acute systemic treatment with E177 (1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally [i.p.]) significantly attenuated the cognitive impairments induced by DIZ in the IAP (all P-values <0.05, n=7), and the protective effect of the most promising dose of E177 (5 mg/kg) was abrogated when H3R agonist R-(α)-methylhistamine (RAMH; 10 mg/kg i.p.) was co-administered (P=0.281 for DIZ-amnesia group vs DIZ + E177 + RAMH group, n=7). The discrimination index calculated for E177 (5 mg/kg, i.p.) showed a significant memory-enhancing effect on DIZ-induced short-term memory impairment in the NOR task (P<0.05, n=6), with the enhancement nullified when animals were co-administered RAMH (10 mg/kg). Moreover, the results revealed that E177 (5 and 10 mg/kg, i.p.) did not alter the anxiety levels and locomotor activity of animals naïve to the open-field test (all P-values >0.05, n=8) or the elevated plus maze test (all P-values >0.05, n=6-8), which indicated that the E177-induced enhancement of memory performance in the IAP or NOR task was unrelated to changes in emotional response or in spontaneous locomotor activity.
Conclusion: The observed results suggested a possible contribution of H3Rs in the alteration of brain neurotransmitters that accompany neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD.
Keywords: Histamine H3 receptors; antagonist; anxiety; dizocilpine-induced amnesia; elevated plus maze; inhibitory avoidance paradigm; memory; novel object recognition; open field test.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist E159 Reverses Memory Deficits Induced by Dizocilpine in Passive Avoidance and Novel Object Recognition Paradigm in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 12;8:709. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00709. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29075190 Free PMC article.
-
The dual-acting AChE inhibitor and H3 receptor antagonist UW-MD-72 reverses amnesia induced by scopolamine or dizocilpine in passive avoidance paradigm in rats.Physiol Behav. 2016 Oct 15;165:383-91. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 27568232
-
The Potent and Selective Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist E169 Counteracts Cognitive Deficits and Mitigates Disturbances in the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in MK801-Induced Amnesia in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 12;24(16):12719. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612719. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628900 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorating effects of histamine H3 receptor antagonist E177 on acute pentylenetetrazole-induced memory impairments in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2021 May 7;405:113193. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113193. Epub 2021 Feb 21. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33626390
-
Histamine H3 receptor as a potential target for cognitive symptoms in neuropsychiatric diseases.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Oct 1;312:415-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.051. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27363923 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Neuroinflammation in Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Emergence of Brain Histaminergic System. Lessons Also for BPSD?Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 16;11:886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00886. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32612529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neuroprotective Effects of Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist E177 on Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in Rats.Molecules. 2019 Nov 14;24(22):4106. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224106. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31739417 Free PMC article.
-
The Dual-Active Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist and Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitor E100 Alleviates Autistic-Like Behaviors and Oxidative Stress in Valproic Acid Induced Autism in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 3;21(11):3996. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113996. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32503208 Free PMC article.
-
Histaminergic neurotransmission in aging and Alzheimer's disease: A review of therapeutic opportunities and gaps.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2023 Apr 25;9(2):e12379. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12379. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37123051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Blockade of Histamine H3 Receptors and Inhibition of Acetylcholine Esterase Alleviate Autistic-Like Behaviors in BTBR T+ tf/J Mouse Model of Autism.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 28;10(9):1251. doi: 10.3390/biom10091251. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32872194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kivipelto M, Mangialasche F, Ngandu T. Lifestyle interventions to prevent cognitive impairment, dementia and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14(11):653–666. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki T, Katsumata Y, Arai A. Association between changes in the use of psychotropic drugs and behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia over 1 year among long-term care facility residents. Psychogeriatrics. 2018 Oct;:18. Epub. - PubMed
-
- Shaik JB, Palaka BK, Penumala M, et al. Synthesis, pharmacological assessment, molecular modeling and in silico studies of fused tricyclic coumarin derivatives as a new family of multifunctional anti-Alzheimer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;107:219–232. - PubMed
-
- Khunnawutmanotham N, Chimnoi N, Saparpakorn P, Techasakul S. Synthesis and anti-acetylcholinesterase activity of scopoletin derivatives. Bioorg Chem. 2016;65:137–145. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

