Irreversible electroporation combined with chemotherapy for unresectable pancreatic carcinoma: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 30863100
- PMCID: PMC6388995
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S186721
Irreversible electroporation combined with chemotherapy for unresectable pancreatic carcinoma: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to determine the safety and efficacy of irreversible electroporation (IRE) combined with chemotherapy for unresectable pancreatic carcinoma (stage III/IV).
Methods: We prospectively enrolled 54 patients (30 men; median age 61.0 years; range 41-73 years) undergoing IRE with or without chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer between July 2015 and August 2016. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to analyze progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Safety was assessed based on the occurrence of adverse events.
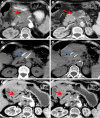
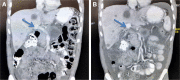
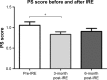
Results: All patients successfully underwent IRE. Major IRE-related complications were observed in four patients (7.4%). Gastrointestinal hemorrhage only developed in cases undergoing IRE via the open method, and was successfully managed with interventional embolization and/or vascular ligation. Any minor complications in the cases were alleviated within 14 days after symptomatic treatment. Overall, the performance status score decreased from 1.06 to 0.89 at 3 months after IRE (P<0.05). Among those with stage III disease, after a median follow-up of 18.8 months (range 9.6-28.7 months), the median OS from diagnosis was 16.2 and 20.3 months in the IRE and IRE + Chemo groups, respectively. Among those with stage IV disease, after a median follow-up of 13.3 months (range 3.7-23.1 months), the median OS from diagnosis was 11.6 and 13.56 months in the IRE and IRE + Chemo groups, respectively. The OS was significantly poorer in the IRE group than in the IRE + Chemo group (log-rank test, P=0.0398).
Conclusion: Patients with pancreatic carcinoma could benefit from IRE, which improved the OS in certain patients who had also undergone chemotherapy. Although some severe complications were noted, IRE was generally well tolerated.
Keywords: ablation; irreversible electroporation; overall survival; pancreatic carcinoma; progression-free survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An important discovery on combination of irreversible electroporation and allogeneic natural killer cell immunotherapy for unresectable pancreatic cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 19;8(60):101795-101807. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21974. eCollection 2017 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29254205 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer with Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation: Results of the Phase I/II PANFIRE Study.Radiology. 2017 Feb;282(2):585-597. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016152835. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Radiology. 2017. PMID: 27604035 Clinical Trial.
-
[Combining intraoperative ultrasound-guided irreversible electroporation with chemotherapy for treating locally advanced pancreatic cancer: a clinical report of 64 cases].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 1;58(10):787-792. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20200331-00270. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32993267 Chinese.
-
Multicenter randomized controlled trial and registry study to assess the safety and efficacy of the NanoKnife® system for the ablation of stage 3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma: overview of study protocols.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jul 7;21(1):785. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08474-4. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34233640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review of Irreversible Electroporation Role in Management of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 3;11(11):1718. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111718. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31684186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer-An Evolving Experimental and Clinical Method.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4381. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054381. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of Current Clinical Outcomes, Mechanism of Action and Opportunities for Synergistic Therapy.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 10;10(8):1609. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081609. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33920118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folate Intake and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Studies.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Jul;66(7):2368-2379. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06525-7. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 32770489
-
Irreversible electroporation for liver metastasis from pancreatic cancer: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Jan 26;8(2):390-397. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i2.390. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 32047790 Free PMC article.
-
Novel combination of irreversible electroporation and allogenic chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy synergizes therapeutic outcomes in a preclinical human pancreatic cancer mouse model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 12:2025.08.10.669537. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.10.669537. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40832328 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Baron TH, Kozarek RA. Preoperative biliary stents in pancreatic cancer – proceed with caution. N Engl J Med Overseas Ed. 2010;362(2):170–172. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. - PubMed
-
- Jooste V, Dejardin O, Bouvier V, et al. Pancreatic cancer: wait times from presentation to treatment and survival in a population-based study. Int J Cancer. 2016;139(5):1073–1080. - PubMed
-
- Smeenk HG, Tran TC, Erdmann J, van Eijck CH, Jeekel J. Survival after surgical management of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: does curative and radical surgery truly exist? Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005;390(2):94–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

