Exploring Impact of Rare Variation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by a Genome Wide Imputation Approach
- PMID: 30863397
- PMCID: PMC6399402
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00258
Exploring Impact of Rare Variation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by a Genome Wide Imputation Approach
Abstract
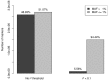
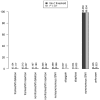
The importance of low frequency and rare variation in complex disease genetics is difficult to estimate in patient populations. Genome-wide association studies are therefore, underpowered to detect rare variation. We have used a combined approach of genome-wide-based imputation with a highly stringent sequence kernel association (SKAT) test and a case-control burden test. We identified 98 candidate genes containing rare variation that in aggregate show association with SLE many of which have recognized immunological function, but also function and expression related to relevant tissues such as the joints, skin, blood or central nervous system. In addition we also find that there is a significant enrichment of genes annotated for disease-causing mutations in the OMIM database, suggesting that in complex diseases such as SLE, such mutations may be involved in subtle or combined phenotypes or could accelerate specific organ abnormalities found in the disease. We here provide an important resource of candidate genes for SLE.
Keywords: GWAS—genome-wide association study; SLE; aggregated case-control enrichment; imputated rare variation; sequence kernel association test; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures