Intermittent Hypoxia Composite Abnormal Glucose Metabolism-Mediated Atherosclerosis In Vitro and In Vivo: The Role of SREBP-1
- PMID: 30863480
- PMCID: PMC6378806
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4862760
Intermittent Hypoxia Composite Abnormal Glucose Metabolism-Mediated Atherosclerosis In Vitro and In Vivo: The Role of SREBP-1
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to establish a 3T3-L1 adipocyte model and ApoE-/- mouse model of intermittent hypoxia (IH) composite abnormal glucose metabolism (AGM) in vitro and in vivo and explore their synergistic damage effect leading to atherosclerosis (AS) and the influence of SREBP-1 signaling molecule-related mechanisms.
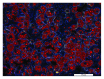
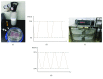
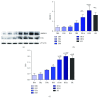
Methods: Mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes were cultured with complete culture medium containing DEX 1 × 106 mol/L for 96 h to establish an AGM-3T3-L1 adipocyte model. Then, AGM-3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with IH for 0 cycles, 2 cycles, 4 cycles, 8 cycles, 16 cycles, and 32 cycles and sustained hypoxia (SH). ApoE-/- mice were treated with high-fat diet and injection of STZ solution to establish an AGM-ApoE-/- mouse model. A total of 16 AGM-ApoE-/- mice were randomly and averagely divided into the normoxic control group (NC) and model group (CIH). AGM-ApoE-/- mice of the CIH group were treated with IH, which meant that the oxygen concentration fell to 10 ± 0.5% in the first 90 seconds of one cycle and then increased to 21 ± 0.5% in the later 90 seconds, continuous for eight hours per day (09 : 00-17 : 00) with a total of eight weeks. Eight C57BL/6J mice were used as the blank control group (Con) which was fed with conventional diet. qPCR and Western blotting were used to detect the expression level of SREBP-1c, FAS, and IRS-1. Oil Red O staining was used to compare the plaque of the aorta among each mouse group.
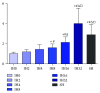
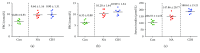
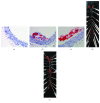
Results: As a result, within 32 cycles of IH, mRNA and protein expression levels of SREBP-1c and FAS in AGM-3T3-L1 adipocytes were elevated with the increase in IH cycles; the mRNA expression of IRS-1 was decreased after IH 32 cycles and lower than that of the SH group. For the study in vivo, Oil Red O staining showed a more obvious AS aortic plaque in the CIH group. After CIH treatment of 4 w and 8 w, fasting blood glucose (FBG) of the NC group and CIH group was higher than that of the Con group, and the insulin level of the CIH group was higher than that of the Con group after IH treatment of 8 w. The expressions of the IRS-1 mRNA level in the aorta, skeletal muscle, and liver of the CIH group were lower than those in the Con group. The mRNA and protein expression of SREBP-1c and its downstream molecule FAS in the aorta, skeletal muscle, and liver significantly enhanced in the CIH group in contrast with those in the Con group.
Conclusion: The CIH composite AGM could promote the progress of AS, which might be related to the modulation of the expression of SREBP-1-related molecular pathways.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

