Discovery of Actinomycetes from Extreme Environments with Potential to Produce Novel Antibiotics
- PMID: 30863668
- PMCID: PMC6393050
- DOI: 10.5195/cajgh.2018.337
Discovery of Actinomycetes from Extreme Environments with Potential to Produce Novel Antibiotics
Abstract
Introduction: Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens pose serious challenges to healthcare institutions and health of the public. Thus, there is an urgent need for the discovery of new and effective antimicrobial agents. Microorganisms that exist in extreme environments such as those with high salinity or alkalinity, are known as extremophiles, and include various species of actinomycetes. The goal of this study is to discover novel antibiotics from extremophiles found in Kazakhstan that are effective against drug resistant pathogens.
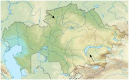
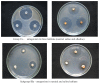
Methods: Soil from extreme environments of Kazakhstan was collected, and pure cultures of actinomycetes were isolated and cultured in modified Bennett's broth with either high concentrations of salt or high pH to mimic extreme environments. Extracts obtained from selected actinomycetes strains were used to test for antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Aspergillus niger.
Results: A total of 5936 strains of extremophile actinomycetes were isolated; from these, 2019 strains were further isolated into pure cultures. Of these, 415 actinomycetes strains that demonstrated antagonistic antibacterial activities were selected. These actinomycetes were further classified into groups and subgroups based on their responses to different culture conditions. Antimicrobial antagonism activity for some of the actinomycetes strains was dependent on culture conditions and development of aerial mycelia under extreme conditions.
Conclusion: We identified several interesting candidate extracts with putative antimicrobial activities against several strains of drug resistant pathogens. Our research of the actinomycetes' ability to produce antibiotics in the near-natural conditions provides a great opportunity to assess their biodiversity and distribution in the Central Asian region and to develop new methodological approaches to the screening of new antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: Actinomycetes; Antibiotic Resistance; Antibiotics; Extremophiles; Natural Products; Pathogens.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Beyond traditional screening: Unveiling antibiotic potentials of actinomycetes in extreme environments.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 13;10(22):e40371. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40371. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39641013 Free PMC article.
-
Potentials of Actinomycetes from Reserved Environments as Antibacterial Agents Against Drug-Resistant Clinical Bacterial Strains.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020 Mar;30(2):251-258. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v30i2.13. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 32165815 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizationharacterization of Extremophilic Actinomycetes Strains as Sources of Antimicrobial Agents.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2296:59-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1358-0_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33977442
-
Exploring the diversity and antimicrobial potential of actinomycetes isolated from different environments in Saudi Arabia: a systematic review.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1568899. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1568899. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40207161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actinomycetes, an Inexhaustible Source of Naturally Occurring Antibiotics.Antibiotics (Basel). 2018 May 24;7(2):45. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7020045. Antibiotics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29795019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism-Based Approach to New Antibiotic Producers Screening among Actinomycetes in the Course of the Citizen Science Project.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 5;11(9):1198. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091198. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139977 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on Antibacterial Activity and Diversity of Cultivable Actinobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Soil in Futian and Maoweihai of China.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Jun 9;2019:3476567. doi: 10.1155/2019/3476567. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31281398 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond traditional screening: Unveiling antibiotic potentials of actinomycetes in extreme environments.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 13;10(22):e40371. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40371. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39641013 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activities of extremophilic actinomycetes extracts from Kazakhstan's unique ecosystems against influenza viruses and paramyxoviruses.Virol J. 2019 Dec 2;16(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1254-1. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31791359 Free PMC article.
-
Potentials of Actinomycetes from Reserved Environments as Antibacterial Agents Against Drug-Resistant Clinical Bacterial Strains.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020 Mar;30(2):251-258. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v30i2.13. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 32165815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer RS, Finch R, Wegener HC, Bywater R, Walters J, Lipsitch M. Antibiotic resistance--the interplay between antibiotic use in animals and human beings. The Lancet Infectious diseases. 2003;3(1):47–51. - PubMed
-
- Talbot GH, Bradley J, Edwards JE, Jr, Gilbert D, Scheld M, Bartlett JG. Bad bugs need drugs: an update on the development pipeline from the Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2006;42(5):657–668. - PubMed
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. Journal of natural products. 2007;70(3):461–477. - PubMed
-
- Tobias Kieser MJB, Buttner Mark J, Chater Keith F, Hopwood David A. Practical Streptomyces Genetics. [Accessed 11 Jul, 2018]. https://www.jic.ac.uk/science/molmicro/Strepmanual/Manual.htm.
-
- Demain AL. Pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites of microorganisms. Applied microbiology and biotechnology. 1999;52(4):455–463. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
