Characterization of Arabinosyl Transfer Reactions in the Biosynthesis of Mycobacterial Cell Envelope (Lipo)Polysaccharides
- PMID: 30864132
- PMCID: PMC6432646
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9154-9_14
Characterization of Arabinosyl Transfer Reactions in the Biosynthesis of Mycobacterial Cell Envelope (Lipo)Polysaccharides
Abstract
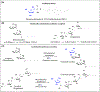
D-Arabinofuranose is a major glycosyl constituent of mycobacteria found in two essential cell envelope heteropolysaccharides, arabinogalactan and lipoarabinomannan. Seven different arabinosyltransferases at least are required to synthesize the arabinan domain of these two major glycans. Because of their interest from the perspective of drug development, these enzymes have been the object of intense investigations. In this chapter, we describe the protocols used to perform nonradioactive arabinosyltransferase assays with synthetic acceptor and donor substrates and characterize the enzymatic products of the reactions by mass spectrometry.
Keywords: Arabinosyltransferase; D-Arabinose; Lipid donor; Mycobacteria; Synthetic arabinoside acceptor.
Figures
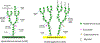
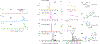
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2016, WHO Press.
-
- Queiroz A, and Riley LW (2017) Bacterial immunostat: Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipids and their role in the host immune response, Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 50, 9–18. - PubMed
-
- Brennan PJ, and Nikaido H (1995) The envelope of mycobacteria, Annu Rev Biochem 64, 29–63. - PubMed
-
- Lohrasbi V, Talebi M, et al. (2017) Trends in the discovery of new drugs for Mycobacterium tuberculosis therapy with a glance at resistance, Tuberculosis - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

