Bile Acid Homeostasis in a Cholesterol 7α-Hydroxylase and Sterol 27-Hydroxylase Double Knockout Mouse Model
- PMID: 30864232
- PMCID: PMC7893641
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.30612
Bile Acid Homeostasis in a Cholesterol 7α-Hydroxylase and Sterol 27-Hydroxylase Double Knockout Mouse Model
Abstract
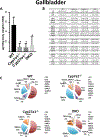
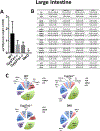
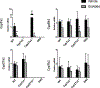
Bile acids (BAs) are diverse molecules that are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver. The synthesis of BAs has traditionally been shown to occur through two pathways. Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) performs the initial and rate-limiting step in the classical pathway, and sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) initiates the hydroxylation of cholesterol in the alternative pathway. While the role of individual BA species as physiological detergents is relatively ubiquitous, their endocrine functions as signaling molecules and roles in disease pathogenesis have been emerging to be BA species-specific. In order to better understand the pharmacologic and toxicologic roles of individual BA species in an in vivo model, we created cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (Cyp7a1) and sterol 27-hydroxylase (Cyp27a1) double knockout (DKO) mice by cross-breeding single knockout mice (Cyp7a1-/- and Cyp27a1-/- ). BA profiling and quantification by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of serum, gallbladder, liver, small intestine, and colon of wild-type, Cyp7a1-/- , Cyp27a1-/- , and DKO mice showed that DKO mice exhibited a reduction of BAs in the plasma (45.9%), liver (60.2%), gallbladder (76.3%), small intestine (88.7%), and colon (93.6%), while maintaining a similar BA pool composition compared to wild-type mice. The function of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) in DKO mice was lower, revealed by decreased mRNA expression of well-known FXR target genes, hepatic small heterodimer partner, and ileal fibroblast growth factor 15. However, response to FXR synthetic ligands was maintained in DKO mice as treatment with GW4064 resulted in similar changes in gene expression in all strains of mice. Conclusion: We provide a useful tool for studying the role of individual BAs in vivo; DKO mice have a significantly reduced BA pool, have a similar BA profile, and maintained response to FXR activation.
© 2019 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures




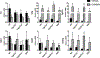
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

