Psychological distress and its association with socio-demographic factors in a rural district in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 30865656
- PMCID: PMC6415806
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212765
Psychological distress and its association with socio-demographic factors in a rural district in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Psychological distress including depression and anxiety are among the most serious causes of morbidity and mortality in Bangladesh. There has been no study in the rural area to report the prevalence of and risk factors for psychological distress. The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence of and risk factors for psychological distress in a rural district in Bangladesh.
Methods: A total of 2425 adults (1249 women) aged 18-90 years were selected from the Narail upazilla using multi-level cluster random sampling for a cross-sectional study. Psychological distress was assessed using the Kessler 10 items questionnaire. Participants' socio-demographic status, life style factors and health conditions were also collected. Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for binary outcomes and mean changes for continuous outcomes of psychological distress score were computed. Logistic regression and generalized linear model techniques were used for analytical purpose.
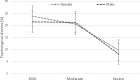
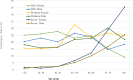
Results: The overall prevalence of psychological distress was 52.5%. This proportion included 22.7% people rated as having mild psychological distress, 20.8% moderate and 9.0% severe. The prevalence of moderate (24.7% vs. 17.5%, p<0.001) and severe (16.2% vs. 2.5%, p<0.001) psychological distress was significantly higher in older adults of age 60-90 years than that in younger adults of age 18-59 years. The prevalence of severe psychological distress was higher in females than males and the difference increased with age (vs. (females vs males: 1.9% vs. 1.1% at age of <30 years, 12.2% vs. 10.1% at age between 60-69 years, and 45.5% vs. 25.4% at age of 80 years or older). After multivariate adjustment, compared to degree or equivalent level of education, no education (odds ratio (OR), 1.71, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.03-2.82) was associated with higher prevalence of any psychological distress in the total sample. Compared to married, psychological distress among widowed older adults was almost five times higher prevalence (OR, 4.89, 95% CI, 2.51-9.55). Socio-economic status showed a U-shaped relationship with the prevalence of psychological distress; being very poor or wealthy was associated with higher prevalence of psychological distress compared to those of moderate socio-economic status. People living in pourashava (semi-urban areas) reported significantly higher prevalence of psychological distress compared to people living in typical rural unions.
Conclusions: In this rural Bangladeshi community, the prevalence of psychological distress was high, especially among older women. Factors including lower level of education, inability to work, and living in semi-urban areas were associated with higher prevalence of psychological distress. Public health programmes should target people in high risk groups to reduce their psychological distress in Bangladesh.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. "Depression: let’s talk" says WHO, as depression tops list of causes of ill health. 2017.
-
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 (GBD 2016) Seattle, United States: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), 2017. 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical