Convolutional neural network for cell classification using microscope images of intracellular actin networks
- PMID: 30865716
- PMCID: PMC6415833
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213626
Convolutional neural network for cell classification using microscope images of intracellular actin networks
Abstract
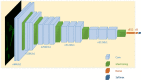
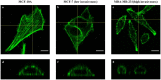
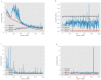
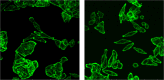
Automated cell classification is an important yet a challenging computer vision task with significant benefits to biomedicine. In recent years, there have been several studies attempted to build an artificial intelligence-based cell classifier using label-free cellular images obtained from an optical microscope. Although these studies showed promising results, such classifiers were not able to reflect the biological diversity of different types of cell. While in terms of malignant cell, it is well-known that intracellular actin filaments are altered substantially. This is thought to be closely related to the abnormal growth features of tumor cells, their ability to invade surrounding tissues and also to metastasize. Therefore, being able to classify different types of cell based on their biological behaviors using automated technique is more advantageous. This article reveals the difference in the actin cytoskeleton structures between breast normal and cancer cells, which may provide new information regarding malignant changes and be used as additional diagnostic marker. Since the features cannot be well detected by human eyes, we proposed the application of convolutional neural network (CNN) in cell classification based on actin-labeled fluorescence microscopy images. The CNN was evaluated on a large number of actin-labeled fluorescence microscopy images of one human normal breast epithelial cell line and two types of human breast cancer cell line with different levels of aggressiveness. The study revealed that the CNN performed better in the cell classification task compared to a human expert.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Breast Cancer Identification via Thermography Image Segmentation with a Gradient Vector Flow and a Convolutional Neural Network.J Healthc Eng. 2019 Nov 3;2019:9807619. doi: 10.1155/2019/9807619. eCollection 2019. J Healthc Eng. 2019. PMID: 31915519 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated local binary pattern texture features for classification of breast tissue imaged by optical coherence microscopy.Med Image Anal. 2017 May;38:104-116. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Med Image Anal. 2017. PMID: 28327449 Free PMC article.
-
Computer assisted recognition of breast cancer in biopsy images via fusion of nucleus-guided deep convolutional features.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Oct;194:105531. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105531. Epub 2020 May 11. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32422473
-
Involvement of Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Image Classification: A Survey.Comput Math Methods Med. 2017;2017:3781951. doi: 10.1155/2017/3781951. Epub 2017 Dec 31. Comput Math Methods Med. 2017. PMID: 29463985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast cancer cell nuclei classification in histopathology images using deep neural networks.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2018 Feb;13(2):179-191. doi: 10.1007/s11548-017-1663-9. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2018. PMID: 28861708 Review.
Cited by
-
Small hand-designed convolutional neural networks outperform transfer learning in automated cell shape detection in confluent tissues.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 16;18(2):e0281931. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281931. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36795738 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Cancer Cell Taxonomy Using an Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;14(9):2224. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092224. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565352 Free PMC article.
-
The Artificial Intelligence-Powered New Era in Pharmaceutical Research and Development: A Review.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Aug 15;25(6):188. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02901-y. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39147952 Review.
-
Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, and Machine Learning to Support the Analysis of Microscopic Images of Cells and Tissues.J Imaging. 2025 Feb 15;11(2):59. doi: 10.3390/jimaging11020059. J Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39997561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Human Protein Atlas Image Classification competition.Nat Methods. 2019 Dec;16(12):1254-1261. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0658-6. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Nat Methods. 2019. PMID: 31780840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cruz-Roa AA, Arevalo Ovalle JE, Madabhushi A, Gonzalez Osorio FA. A deep learning architecture for image representation, visual interpretability and automated basal-cell carcinoma cancer detection. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2013;16(Pt 2):403–10. Epub 2014/03/01. . - PubMed
-
- Meng N, So HKH, Lam EY, editors. Computational single-cell classification using deep learning on bright-field and phase images. 2017 Fifteenth IAPR International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA); 2017 8–12 May 2017.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

