VKORC1 and CYP2C9 Polymorphisms: A Case Report in a Dutch Family with Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 30866412
- PMCID: PMC6429271
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20051160
VKORC1 and CYP2C9 Polymorphisms: A Case Report in a Dutch Family with Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
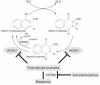
Here, we describe a Dutch family with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We hypothesized that there might be an association between the presence of Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex 1 (VKORC1) and/or cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) variant alleles and the early onset of IPF in the members of this family. VKORC1 (rs9923231 and rs9934438) and CYP2C9 (rs1799853 and rs1057910) were genotyped in this family, which includes a significant number of pulmonary fibrosis patients. In all family members, at least one of the variant alleles tested was present. The presence of the VKORC1 variant alleles in all of the IPF cases and CYP2C9 variants in all but one, which likely leads to a phenotype that is characterized by the early onset and progressive course of IPF. Our findings indicate a role of these allelic variants in (familial) IPF. Therefore, we suggest that the presence of these variants, in association with other pathogenic mutations, should be evaluated during genetic counselling. Our findings might have consequences for the lifestyle of patients with familial IPF in order to prevent the disease from becoming manifest.
Keywords: familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; oxidative stress; polymorphism; vitamin K supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of Genetic Polymorphisms in the VKORC1 and CYP2C9 Genes with Warfarin Dosage in a Group of Kuwaiti Individuals.Mol Diagn Ther. 2016 Apr;20(2):183-90. doi: 10.1007/s40291-016-0190-7. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26940072
-
Linkage disequilibrium between the CYP2C19*2,*17 and CYP2C9*1 alleles and impact of VKORC1, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms and gene-gene interactions on warfarin therapy.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2017 Jan;43(1):124-129. doi: 10.1007/s11239-016-1436-2. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2017. PMID: 27743182
-
Association of gene polymorphisms with the risk of warfarin bleeding complications at therapeutic INR in patients with mechanical cardiac valves.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014 Jun;39(3):314-8. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12143. Epub 2014 Mar 6. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014. PMID: 24602049
-
Pharmacogenetic variants and vitamin K deficiency: a risk factor or trigger for fibrosing interstitial pneumonias?Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018 May;24(3):287-295. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000467. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 29538081 Review.
-
Common single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review.Eur Respir Rev. 2024 Sep 25;33(173):240018. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0018-2024. Print 2024 Jul. Eur Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 39322261 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of vitamin K in the etiology of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019;36(3):251-252. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v36i3.8530. Epub 2019 May 1. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019. PMID: 32476960 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Drug-Gene Risk Stratification in Patients with Suspected Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease.Drug Saf. 2024 Apr;47(4):355-363. doi: 10.1007/s40264-024-01400-0. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Drug Saf. 2024. PMID: 38460070 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin K: Metabolism, Genetic Influences, and Chronic Disease Outcomes.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 17;13(6):e70431. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70431. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40535915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Travis W.D., Costabel U., Hansell D.M., King T.E., Jr., Lynch D.A., Nicholson A.G., Ryerson C.J., Ryu J.H., Selman M., Wells A.U., et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013;188:733–748. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

