Recent Advances in Aptamer Discovery and Applications
- PMID: 30866536
- PMCID: PMC6429292
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24050941
Recent Advances in Aptamer Discovery and Applications
Abstract
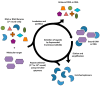
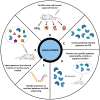
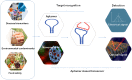
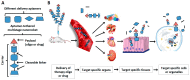
Aptamers are short, single-stranded DNA, RNA, or synthetic XNA molecules that can be developed with high affinity and specificity to interact with any desired targets. They have been widely used in facilitating discoveries in basic research, ensuring food safety and monitoring the environment. Furthermore, aptamers play promising roles as clinical diagnostics and therapeutic agents. This review provides update on the recent advances in this rapidly progressing field of research with particular emphasis on generation of aptamers and their applications in biosensing, biotechnology and medicine. The limitations and future directions of aptamers in target specific delivery and real-time detection are also discussed.
Keywords: aptamer; biosensor; diagnostics; nanorocket; systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX); therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

