Mechanisms of FSH- and Amphiregulin-Induced MAP Kinase 3/1 Activation in Pig Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes During Maturation In Vitro
- PMID: 30866587
- PMCID: PMC6429514
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20051179
Mechanisms of FSH- and Amphiregulin-Induced MAP Kinase 3/1 Activation in Pig Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes During Maturation In Vitro
Abstract
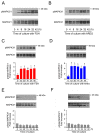
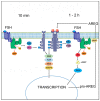
The maturation of mammalian oocytes in vitro can be stimulated by gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating hormone, FSH) or their intrafollicular mediator, epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like peptide-amphiregulin (AREG). We have shown previously that in pig cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs), FSH induces expression and the synthesis of AREG that binds to EGF receptor (EGFR) and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase 3/1 (MAPK3/1) signaling pathway. However, in this study we found that FSH also caused a rapid activation of MAPK3/1 in the cumulus cells, which cannot be explained by the de novo synthesis of AREG. The rapid MAPK3/1 activation required EGFR tyrosine kinase (TK) activity, was sensitive to SRC proto-oncogene non-receptor tyrosine kinase (SRC)-family and protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors, and was resistant to inhibitors of protein kinase A (PKA) and metalloproteinases. AREG also induced the rapid activation of MAPK3/1 in cumulus cells, but this activation was only dependent on the EGFR TK activity. We conclude that in cumulus cells, FSH induces a rapid activation of MAPK3/1 by the ligand-independent transactivation of EGFR, requiring SRC and PKC activities. This rapid activation of MAPK3/1 precedes the second mechanism participating in the generation and maintenance of active MAPK3/1-the ligand-dependent activation of EGFR depending on the synthesis of EGF-like peptides.
Keywords: FSH; amphiregulin; cumulus cells; epidermal growth factor receptor; mitogen-activated protein kinase 3/1; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Positive feedback loop between prostaglandin E2 and EGF-like factors is essential for sustainable activation of MAPK3/1 in cumulus cells during in vitro maturation of porcine cumulus oocyte complexes.Biol Reprod. 2011 Nov;85(5):1073-82. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.090092. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Biol Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21778143
-
Signaling pathways regulating FSH- and amphiregulin-induced meiotic resumption and cumulus cell expansion in the pig.Reproduction. 2012 Nov;144(5):535-46. doi: 10.1530/REP-12-0191. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Reproduction. 2012. PMID: 22949725
-
Hormone-induced expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme/A disintegrin and metalloprotease-17 impacts porcine cumulus cell oocyte complex expansion and meiotic maturation via ligand activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor.Endocrinology. 2007 Dec;148(12):6164-75. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0195. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17901238
-
Regulation of cumulus expansion and hyaluronan synthesis in porcine oocyte-cumulus complexes during in vitro maturation.Endocr Regul. 2012 Oct;46(4):225-35. doi: 10.4149/endo_2012_04_225. Endocr Regul. 2012. PMID: 23127506 Review.
-
The release of EGF domain from EGF-like factors by a specific cleavage enzyme activates the EGFR-MAPK3/1 pathway in both granulosa cells and cumulus cells during the ovulation process.J Reprod Dev. 2012;58(5):510-4. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2012-056. J Reprod Dev. 2012. PMID: 23124701 Review.
Cited by
-
Oocyte-Specific Knockout of Histone Lysine Demethylase KDM2a Compromises Fertility by Blocking the Development of Follicles and Oocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 9;23(19):12008. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912008. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233308 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying selection signatures for immune response and resilience to Aleutian disease in mink using genotype data.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 12;15:1370891. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1370891. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39071778 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MAPK3/1 and AKT in the Acquisition of High Meiotic and Developmental Competence of Porcine Oocytes Cultured In Vitro in FLI Medium.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 15;22(20):11148. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011148. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681809 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Translational Modifications in Oocyte Maturation and Embryo Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 2;9:645318. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645318. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E2/ER signaling mediates the meiotic arrest of goat intrafollicular oocytes induced by follicle-stimulating hormone.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad351. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad351. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37925610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Su Y., Wigglesworth K., Pendola F.L., O’Brien M.J., Eppig J.J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in cumulus cells is essential for gonadotropin-induced oocyte meiotic resumption and cumulus expansion in the mouse. Endocrinology. 2002;143:2221–2232. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.6.8845. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Su Y.Q., Denegre J.M., Wigglesworth K., Pendola F.L., O’Brien M.J., Eppig J.J. Oocyte-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2) in cumulus cells is required for the maturation of the mouse oocyte-cumulus cell complex. Dev. Biol. 2003;263:126–138. doi: 10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00437-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

