Risk factors to identify patients who may not benefit from whole brain irradiation for brain metastases - a single institution analysis
- PMID: 30866972
- PMCID: PMC6417259
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-019-1245-9
Risk factors to identify patients who may not benefit from whole brain irradiation for brain metastases - a single institution analysis
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy plays a major role in the management of brain metastases. This study aimed to identify the subset of patients with multiple brain metastases who may not benefit from whole brain irradiation (WBI) due to a short survival time regardless of treatment.
Methods: We analyzed a total of 339 patient records with brain metastases treated with whole brain radiotherapy from January 2009 to January 2016. External beam radiotherapy techniques were used to deliver 33 Gy in 11 fractions (4 fractions per week) to the whole brain. Eight clinical factors with a potential influence on survival were investigated using the Kaplan-Meier method. All factors with a P < 0.05 in univariate analysis were entered into multivariate analysis using Cox regression.
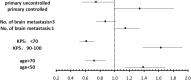
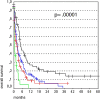
Results: In the present series of 339 patients, median survival time was 2.5 months (M; range, 0-61 months). Four risk factors Karnofsky Performance Score (KPS) < 70, age > 70, > 3 of metastases intracranial, uncontrolled primary tumor) were identified that were significant and negatively correlated with median survival time. Patients with no risk factors had a median survival of 4.7 M; one risk factor, 2.5 M; two risk factors, 2.3 M; and 3-4 risk factors, 0.4 M (p < 0.00001).
Conclusions: Patients with identified risk factors might have a negatively impacted overall survival after WBI. Accordingly, patients who will not benefit from WBI can be easily predicted if they have 3-4 of these risk factors.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; Median survival; Risk factor; Whole brain irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

