The Wave complex controls epidermal morphogenesis and proliferation by suppressing Wnt-Sox9 signaling
- PMID: 30867227
- PMCID: PMC6446834
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201807216
The Wave complex controls epidermal morphogenesis and proliferation by suppressing Wnt-Sox9 signaling
Abstract
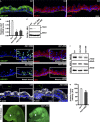
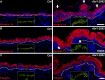
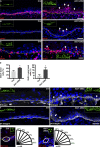
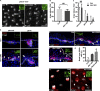
Development of the skin epidermis requires tight spatiotemporal control over the activity of several signaling pathways; however, the mechanisms that orchestrate these events remain poorly understood. Here, we identify a key role for the Wave complex proteins ABI1 and Wave2 in regulating signals that control epidermal shape and growth. In utero RNAi-mediated silencing of Abi1 or Wasf2 induced cellular hyperproliferation and defects in architecture of the interfollicular epidermis (IFE) and delayed hair follicle growth. Unexpectedly, SOX9, a hair follicle growth regulator, was aberrantly expressed throughout the IFE of the mutant embryos, and its forced overexpression mimicked the Wave complex loss-of-function phenotype. Moreover, Wnt signaling, which regulates SOX9+ cell specification, was up-regulated in Wave complex loss-of-function IFE. Importantly, we show that the Wave complex regulates filamentous actin content and that a decrease in actin levels is sufficient to elevate Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Our results identify a novel role for Wave complex- and actin-regulated signaling via Wnt and SOX9 in skin development.
© 2019 Cohen et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hair follicle morphogenesis and epidermal homeostasis in we/we wal/wal mice with postnatal alopecia.Histochem Cell Biol. 2015 May;143(5):481-96. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1291-1. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25366125
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Follicular Outer Root Sheath Cells via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):360-70. doi: 10.1159/000445630. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27352380
-
Abi1 loss drives prostate tumorigenesis through activation of EMT and non-canonical WNT signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Sep 18;17(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0410-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31530281 Free PMC article.
-
Concise Review: Wnt Signaling Pathways in Skin Development and Epidermal Stem Cells.Stem Cells. 2018 Jan;36(1):22-35. doi: 10.1002/stem.2723. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Stem Cells. 2018. PMID: 29047191 Review.
-
Interplay Between SOX9, Wnt/β-Catenin and Androgen Receptor Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 26;20(9):2066. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092066. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31027362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
WASF2 Serves as a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer: A Pan-Cancer Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 14;12:840038. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.840038. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35359421 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and tissue thinning contribute to symmetric cell division in the developing mouse epidermis in a nonautonomous way.PLoS Biol. 2022 Aug 15;20(8):e3001756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001756. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35969606 Free PMC article.
-
Telophase correction refines division orientation in stratified epithelia.Elife. 2019 Dec 13;8:e49249. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49249. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31833472 Free PMC article.
-
Dia1 coordinates differentiation and cell sorting in a stratified epithelium.J Cell Biol. 2022 May 2;221(5):e202101008. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202101008. Epub 2022 Mar 24. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35323863 Free PMC article.
-
A CRISPR knockout screen reveals new regulators of canonical Wnt signaling.Oncogenesis. 2021 Sep 22;10(9):63. doi: 10.1038/s41389-021-00354-7. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 34552058 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

