Injured liver-released miRNA-122 elicits acute pulmonary inflammation via activating alveolar macrophage TLR7 signaling pathway
- PMID: 30867286
- PMCID: PMC6442592
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1814139116
Injured liver-released miRNA-122 elicits acute pulmonary inflammation via activating alveolar macrophage TLR7 signaling pathway
Abstract
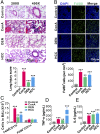
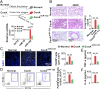
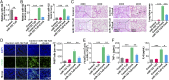
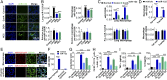
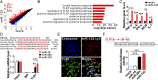
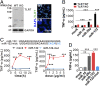
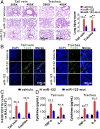
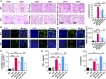
Hepatic injury is often accompanied by pulmonary inflammation and tissue damage, but the underlying mechanism is not fully elucidated. Here we identify hepatic miR-122 as a mediator of pulmonary inflammation induced by various liver injuries. Analyses of acute and chronic liver injury mouse models confirm that liver dysfunction can cause pulmonary inflammation and tissue damage. Injured livers release large amounts of miR-122 in an exosome-independent manner into the circulation compared with normal livers. Circulating miR-122 is then preferentially transported to mouse lungs and taken up by alveolar macrophages, in which it binds Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and activates inflammatory responses. Depleting miR-122 in mouse liver or plasma largely abolishes liver injury-induced pulmonary inflammation and tissue damage. Furthermore, alveolar macrophage activation by miR-122 is blocked by mutating the TLR7-binding GU-rich sequence on miR-122 or knocking out macrophage TLR7. Our findings reveal a causative role of hepatic miR-122 in liver injury-induced pulmonary dysfunction.
Keywords: TLR7/8; circulating miR-122; liver injury; macrophage; pulmonary inflammatory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Huffmyer JL, Nemergut EC. Respiratory dysfunction and pulmonary disease in cirrhosis and other hepatic disorders. Respir Care. 2007;52:1030–1036. - PubMed
-
- Fallon MB, Abrams GA. Pulmonary dysfunction in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2000;32:859–865. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome—A liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2378–2387. - PubMed
-
- Lange PA, Stoller JK. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Lin HI, et al. Reperfusion liver injury induces down-regulation of eNOS and up-regulation of iNOS in lung tissues. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:2203–2206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

