Naomaitai Ameliorated Brain Damage in Rats with Vascular Dementia by PI3K/PDK1/AKT Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 30867669
- PMCID: PMC6379870
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2702068
Naomaitai Ameliorated Brain Damage in Rats with Vascular Dementia by PI3K/PDK1/AKT Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background/aims: Naomaitai can improve blood perfusion and ameliorate the damage in the paraventricular white matter. This study was focused on observing the neuroprotective effect of Naomaitai on the vascular dementia of rat and exploring the action mechanism of PI3K/PDK1/AKT signaling pathway.
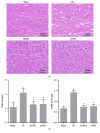
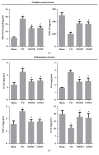
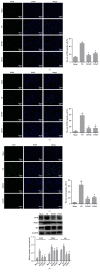
Methods: A vascular dementia model of rats was established by permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion. Rats' behavior was tested by Neurological deficit score and the Morris water maze. The pathology and apoptosis were detected through HE staining and TUNEL assay. Myelin sheath loss and nerve fiber damage were detected by LFB staining. Inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, and brain damage markers were detected through ELISA. The expression of apoptosis-related proteins and PI3K/PDK1/AKT signaling pathway related proteins were measured by western blot. The expressions of PI3K, PDK1, AKT, and MBP in paraventricular white matter cells were detected by immunofluorescence.
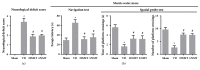
Results: Naomaitai treatment decreased neurological function score in rats with vascular dementia, ameliorated paraventricular white matter damage caused by long-term hypoxia, and hypoperfusion reduced the brain injury markers S-100β and NSE contents, suppressed inflammatory reaction and oxidative stress, reduced IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MDA contents, and remarkably increased IL-10 and SOD contents. TUNEL and western blot assay showed that Naomaitai treatment decreased neuronal cell apoptosis, increased Bcl-2 expression, and reduced caspase-3 and Bax expression. Furthermore, we found Naomaitai inhibited PI3K and PDK1 expression and activated phosphorylated AKT protein in rats with vascular dementia. However, the protective effect of Naomatai in rats with vascular dementia was inhibited, and expression of PI3K signaling pathway-related proteins was blocked after administration of PI3K inhibitor.
Conclusion: Naomaitai can ameliorate brain damage in rats with vascular dementia, inhibit neuronal apoptosis, and have anti-inflammatory and antioxidative stress effects, which may be regulated by the PI3K/PDK1/AKT signaling pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Injury via PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Mar 25;2018:6473580. doi: 10.1155/2018/6473580. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29770336 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles improving the phenotype polarization of microglia via the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 pathway in vascular dementia.Synapse. 2023 Jul;77(4):e22268. doi: 10.1002/syn.22268. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Synapse. 2023. PMID: 36941024
-
3-n-butylphthalide inhibits the apoptosis of nerve cells in rats with cerebral small vessel disease via the PI3K/Akt pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 May;23(10):4474-4480. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201905_17959. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31173324
-
[Acupuncture improves cognitive function of vascular dementia rats by regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Oct 25;46(10):851-6. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200844. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34698459 Chinese.
-
Chemokines play a role in nerve damage and neuroprotection in vascular dementia.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;17:154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.08.002. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39206161 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory microRNAs and vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020 Dec;26(12):1207-1218. doi: 10.1111/cns.13472. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020. PMID: 33459504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brozopine ameliorates cognitive impairment via upregulating Nrf2, antioxidation and anti-inflammation activities.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1428455. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1428455. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39050756 Free PMC article.
-
Production of bioactive recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 12 using a new transient expression vector in E. coli and its neuroprotective effects.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul;105(13):5419-5431. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11430-8. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34244814
-
Insights of Chinese herbal medicine for mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive impairment: Existed evidences and potential directions.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1138566. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138566. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An in-depth study of indolone derivatives as potential lung cancer treatment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 16;15(1):2199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85707-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39820391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalaria R. N. The pathology and pathophysiology of vascular dementia. Neuropharmacology. 2018;134:226–239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

