Luteolin improves heart preservation through inhibiting hypoxia-dependent L-type calcium channels in cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 30867703
- PMCID: PMC6395959
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7214
Luteolin improves heart preservation through inhibiting hypoxia-dependent L-type calcium channels in cardiomyocytes
Abstract
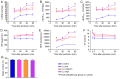
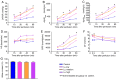
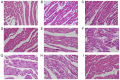
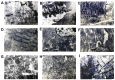
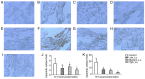
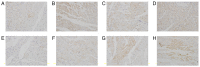
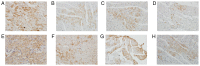
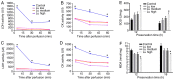
The current study aimed to evaluate whether luteolin could improve long-term heart preservation; this was achieved by evaluating the heart following long-term storage in University of Wisconsin solution (the control group) and in solutions containing three luteolin concentrations. The effects of different preservation methods were evaluated with respect to cardiac function while hearts were in custom-made ex vivo Langendorff perfusion systems. Different preservation methods were evaluated with respect to the histology, ultrastructure and apoptosis rate of the hearts, and the function of cardiomyocytes. In the presence of luteolin, the rate pressure product of the left ventricle was increased within 60 min of reperfusion following a 12-h preservation, coronary flow was higher within 30 min of reperfusion, cardiac contractile function was higher throughout reperfusion following 12- and 18-h preservations, and the left ventricle peak systolic pressure was significantly higher compared with the control group (all P<0.05). The expression levels of apoptosis regulator Bax and apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 in the luteolin groups were significantly decreased and increased, respectively. Lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase and malondialdehyde enzymatic activity was increased following long-term storage, while the activity of superoxide dismutase was significantly decreased. Furthermore, luteolin inhibited L-type calcium currents in ventricular myocytes under hypoxia conditions. Thus, luteolin demonstrated protective effects during long-term heart preservation in what appeared to be a dose-dependent manner, which may be accomplished through inhibiting hypoxia-dependent L-type calcium channels.
Keywords: L-type calcium channel; Langendorff isolated heart perfusion model; apoptosis; heart preservation; luteolin; patch-clamp.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Myocardial protective effects of luteolin on isolated rat heart in hypothermic preservation].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Mar;28(2):154-8. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22737919 Chinese.
-
Luteolin improves contractile function and attenuates apoptosis following ischemia-reperfusion in adult rat cardiomyocytes.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 1;668(1-2):201-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.06.020. Epub 2011 Jun 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21723277
-
Antioxidative effect of luteolin pretreatment on simulated ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiomyocyte and perfused rat heart.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Jul;23(7):518-527. doi: 10.1007/s11655-015-2296-x. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 26956461
-
Effects of luteolin on regulatory proteins and enzymes for myocyte calcium circulation in hypothermic preserved rat heart.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Feb;15(2):1433-1441. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5514. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29399124 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin inhibits apoptosis and improves cardiomyocyte contractile function through the PI3K/Akt pathway in simulated ischemia/reperfusion.Pharmacology. 2011;88(3-4):149-58. doi: 10.1159/000330068. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Pharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21934351
Cited by
-
Navigating Calcium and Reactive Oxygen Species by Natural Flavones for the Treatment of Heart Failure.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 9;12:718496. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.718496. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34858167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidative and Anticancer Potential of Luteolin: A Comprehensive Approach Against Wide Range of Human Malignancies.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jan 19;13(1):e4682. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4682. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39830909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paving Luteolin Therapeutic Potentialities and Agro-Food-Pharma Applications: Emphasis on In Vivo Pharmacological Effects and Bioavailability Traits.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 20;2021:1987588. doi: 10.1155/2021/1987588. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34594472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural L-type calcium channels antagonists from Chinese medicine.Chin Med. 2024 May 21;19(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00944-8. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38773596 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Molecular Mechanism of Erxian Decoction in Treating Osteoporosis Based on Formula Optimization Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jun 18;2021:6641838. doi: 10.1155/2021/6641838. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34239693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Milaniak I, Wilczek-Rużyczka E, Wierzbicki K, Piatek J, Kapelak B, Przybyłowski P. Relationship between satisfaction with social support and self-efficacy and the occurrence of depressive symptoms and stress in heart transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2018;50:2113–2118. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.02.156. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferrera R, Benhabbouche S. Improving donor heart preservation ex vivo. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2011;195:861–881. (In French) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
