MicroRNA-1291 mediates cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by downregulating MED1 in prostate cancer
- PMID: 30867757
- PMCID: PMC6396213
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.9980
MicroRNA-1291 mediates cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by downregulating MED1 in prostate cancer
Abstract
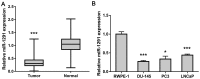
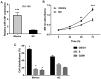
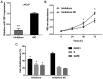
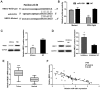
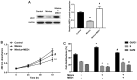
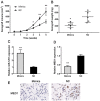
miRNAs are important factors involved in the regulation of tumor development. miR-1291 was found to have regulatory effects in many tumors, but its role in prostate cancer (PCa) still remains unclear. We explored the expression of miR-1291 in PCa to reveal its role in regulating the progression of PCa as well as its underlying mechanism. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the expression of miR-1291 in PCa tissues and cell lines compared to normal tissues and cell lines. miR-1291 mimics and inhibitors were applied to overexpress or inhibit the level of miR-1291 in PCa cells. The ability of cell proliferation was measured using MTT assay, and cell cycle distribution was determined by flow cytometry. The potential target of miR-1291 was identified via western blot analysis and luciferase assays. Then a xenograft model was established to explore the function of miR-1291 in PCa in vivo. The results revealed that the expression level of miR-1291 was significantly lower in the PCa tissues than that in the normal adjacent tissues. In PCa-derived cells, there was also a downregulated expression level of miR-1291. Overexpression of miR-1291 obviously inhibited DU-145 cell proliferation and induced cell cycle transition from G0/G1 to S phase. However, inhibition of miR-1291 promoted the growth of LNCaP cells, and promoted the cell cycle transition to S phase and G2/M phase. MED1 was proven to be a potential target gene of miR-1291, and miR-1291 significantly inhibited its expression. At the in vivo level, overexpression of miR-1291 inhibited the growth of xenograft tumors and significantly inhibited the expression of MED1 protein. Our study demonstrated that miR-1291 inhibits cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of PCa via MED1, which might provide a novel target for PCa diagnosis and biological therapy.
Keywords: MED1; miR-1291; proliferation; prostate cancer; tumorigenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Garisto JD, Klotz L. Active surveillance for prostate cancer: How to do it right. Oncology (Williston Park) 2017;31:333–340, 345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
