A cytosine modification mechanism revealed by the structure of a ternary complex of deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase from bacteriophage T4 with its cofactor and substrate
- PMID: 30867918
- PMCID: PMC6400193
- DOI: 10.1107/S2052252518018274
A cytosine modification mechanism revealed by the structure of a ternary complex of deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase from bacteriophage T4 with its cofactor and substrate
Abstract
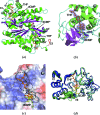
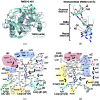
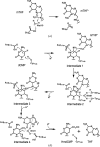
To protect viral DNA against the host bacterial restriction system, bacterio-phages utilize a special modification system - hydroxymethylation - in which dCMP hydroxymethylase (dCH) converts dCMP to 5-hydroxymethyl-dCMP (5hm-dCMP) using N5,N10-methylenetetrahydrofolate as a cofactor. Despite shared similarity with thymidylate synthase (TS), dCH catalyzes hydroxylation through an exocyclic methylene intermediate during the last step, which is different from the hydride transfer that occurs with TS. In contrast to the extensively studied TS, the hydroxymethylation mechanism of a cytosine base is not well understood due to the lack of a ternary complex structure of dCH in the presence of both its substrate and cofactor. This paper reports the crystal structure of the ternary complex of dCH from bacteriophage T4 (T4dCH) with dCMP and tetrahydrofolate at 1.9 Å resolution. The authors found key residues of T4dCH for accommodating the cofactor without a C-terminal tail, an optimized network of ordered water molecules and a hydrophobic gating mechanism for cofactor regulation. In combination with biochemical data on structure-based mutants, key residues within T4dCH and a substrate water molecule for hydroxymethylation were identified. Based on these results, a complete enzyme mechanism of dCH and signature residues that can identify dCH enzymes within the TS family have been proposed. These findings provide a fundamental basis for understanding the pyrimidine modification system.
Keywords: bacteriophage T4; cytosine modification; deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase; thymidylate synthase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A host dTMP-bound structure of T4 phage dCMP hydroxymethylase mutant using an X-ray free electron laser.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 8;9(1):16316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52825-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31705139 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase from bacteriophage T4, a component of the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate-synthesizing complex.EMBO J. 1999 Mar 1;18(5):1104-13. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.5.1104. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10064578 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence from 18O exchange studies for an exocyclic methylene intermediate in the reaction catalyzed by T4 deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase.Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10521-6. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a038. Biochemistry. 1994. PMID: 8068692
-
Enzyme interactions involving T4 phage-coded thymidylate synthase and deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;338:563-70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2960-6_115. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993. PMID: 8304181 Review. No abstract available.
-
Thymidylate synthase: structure, inhibition, and strained conformations during catalysis.Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Oct-Dec;76(1-3):29-43. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(97)00099-5. Pharmacol Ther. 1997. PMID: 9535167 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Broad Host Range Phage Infecting Alteromonas.Viruses. 2021 May 26;13(6):987. doi: 10.3390/v13060987. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34073246 Free PMC article.
-
A host dTMP-bound structure of T4 phage dCMP hydroxymethylase mutant using an X-ray free electron laser.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 8;9(1):16316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52825-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31705139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwalla, S., LaPorte, S., Liu, L., Finer-Moore, J., Stroud, R. M. & Santi, D. V. (1997). Biochemistry, 36, 15909–15917. - PubMed
-
- Berkner, K. L. & Folk, W. R. (1977). J. Biol. Chem. 252, 3185–3193. - PubMed
-
- Borst, P. & Sabatini, R. (2008). Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 62, 235–251. - PubMed
-
- Butler, M. M., Graves, K. L. & Hardy, L. W. (1994). Biochemistry, 33, 10521–10526. - PubMed
-
- Carreras, C. W. & Santi, D. V. (1995). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 64, 721–762. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

