Different Inhibitory Interneuron Cell Classes Make Distinct Contributions to Visual Contrast Perception
- PMID: 30868104
- PMCID: PMC6414440
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0337-18.2019
Different Inhibitory Interneuron Cell Classes Make Distinct Contributions to Visual Contrast Perception
Abstract
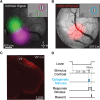
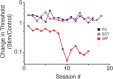
While recent work has revealed how different inhibitory interneurons influence responses of cortical neurons to sensory stimuli, little is known about their distinct contributions to sensory perception. Here, we optogenetically activated different genetically defined interneurons [parvalbumin (PV), somatostatin (SST), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)] in visual cortex (V1) of mice working at threshold in a contrast increment detection task. The visual stimulus was paired with optogenetic stimulation to assess how enhancing V1 inhibitory neuron activity during visual processing altered task performance. PV or SST activation impaired, while VIP stimulation improved, contrast increment detection. The impairment produced by PV or SST activation persisted over several weeks of testing. In contrast, mice learned to reliably detect VIP activation in the absence of any natural visual stimulus. Thus, different inhibitory signals make distinct contributions to visual contrast perception.
Keywords: inhibition; interneurons; mouse; psychophysics; vision; visual contrast.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reliable Sensory Processing in Mouse Visual Cortex through Cooperative Interactions between Somatostatin and Parvalbumin Interneurons.J Neurosci. 2021 Oct 20;41(42):8761-8778. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3176-20.2021. Epub 2021 Sep 7. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34493543 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition by Somatostatin Interneurons in Olfactory Cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2016 Aug 17;10:62. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2016.00062. eCollection 2016. Front Neural Circuits. 2016. PMID: 27582691 Free PMC article.
-
Divisive Inhibition Prevails During Simultaneous Optogenetic Activation of All Interneuron Subtypes in Mouse Primary Visual Cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2019 May 28;13:40. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00040. eCollection 2019. Front Neural Circuits. 2019. PMID: 31191259 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory interneurons in visual cortical plasticity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Oct;73(19):3677-91. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2264-4. Epub 2016 May 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27193323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Current Status of Somatostatin-Interneurons in Inhibitory Control of Brain Function and Plasticity.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:8723623. doi: 10.1155/2016/8723623. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27403348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity and Function of Somatostatin-Expressing Interneurons in the Cerebral Cortex.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 17;20(12):2952. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122952. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Distinct inhibitory neurons differently shape neuronal codes for sound intensity in the auditory cortex".bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 27:2023.02.01.526470. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.01.526470. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Jan 8;45(2):e1502232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1502-23.2024. PMID: 36778269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
VIP interneurons regulate cortical size tuning and visual perception.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113088. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113088. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37682710 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying gain modulation in the cortex.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Feb;21(2):80-92. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0253-y. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31911627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local stimulation of pyramidal neurons in deep cortical layers of anesthetized rats enhances cortical visual information processing.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):22862. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73995-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39354096 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
