Quantitative regulation of the dynamic steady state of actin networks
- PMID: 30869077
- PMCID: PMC6417862
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.42413
Quantitative regulation of the dynamic steady state of actin networks
Abstract
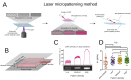
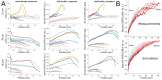
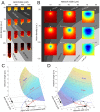
Principles of regulation of actin network dimensions are fundamentally important for cell functions, yet remain unclear. Using both in vitro and in silico approaches, we studied the effect of key parameters, such as actin density, ADF/Cofilin concentration and network width on the network length. In the presence of ADF/Cofilin, networks reached equilibrium and became treadmilling. At the trailing edge, the network disintegrated into large fragments. A mathematical model predicts the network length as a function of width, actin and ADF/Cofilin concentrations. Local depletion of ADF/Cofilin by binding to actin is significant, leading to wider networks growing longer. A single rate of breaking network nodes, proportional to ADF/Cofilin density and inversely proportional to the square of the actin density, can account for the disassembly dynamics. Selective disassembly of heterogeneous networks by ADF/Cofilin controls steering during motility. Our results establish general principles on how the dynamic steady state of actin network emerges from biochemical and structural feedbacks.
Keywords: ADF/Cofilin; actin; actin disassembly; actin network length; cell biology; none.
© 2019, Manhart et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AM, TI, CG, TK, RB, MT, LB, AM No competing interests declared
Figures










References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

