Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus biphasic insulin aspart 30 in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes: A phase III, open-label, 2:1 randomized, treat-to-target trial
- PMID: 30869183
- PMCID: PMC6617768
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13703
Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus biphasic insulin aspart 30 in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes: A phase III, open-label, 2:1 randomized, treat-to-target trial
Abstract
Aims: To assess the efficacy and safety of twice-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) versus biphasic insulin aspart 30 (BIAsp 30) twice daily, both ± metformin, in Chinese adults (N = 543) with type 2 diabetes (T2D) inadequately controlled on premixed/self-mixed or basal insulin ± metformin.
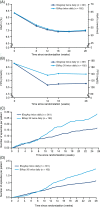
Materials and methods: We conducted a 26-week, phase III, open-label, treat-to-target, 2:1 randomized trial. Hierarchical testing was used with non-inferiority of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) change from baseline to week 26 as the primary endpoint and superiority for the confirmatory secondary endpoints which were as follows: change from baseline in fasting plasma glucose (FPG); nocturnal confirmed hypoglycaemic episodes (12:01-5:59 am, inclusive); total confirmed hypoglycaemic episodes (severe or plasma glucose <3.1 mmol/L with/without symptoms); body weight; and percentage of responders (HbA1c <53 mmol/mol [<7.0%]) without confirmed hypoglycaemic episodes.
Results: Non-inferiority for change from baseline to week 26 in HbA1c and superiority of IDegAsp twice daily versus BIAsp 30 twice daily for change in FPG, nocturnal confirmed and total confirmed hypoglycaemic episodes, was demonstrated. Estimated rates of nocturnal confirmed and total confirmed hypoglycaemic episodes were 47% and 43% lower, respectively, with IDegAsp twice daily versus BIAsp 30 twice daily. Superiority for change in body weight was not confirmed. Participants were more likely to reach the HbA1c goal of <53 mmol/mol (<7.0%) without confirmed hypoglycaemia with IDegAsp twice daily versus BIAsp 30 twice daily by trial end. No new safety signals were identified.
Conclusions: The efficacy and safety of IDegAsp in Chinese patients with T2D was demonstrated, confirming results from international trials.
Keywords: biphasic insulin aspart; insulin aspart; insulin degludec; insulin treatment; intensive insulin therapy; type 2 diabetes.
© 2019 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.N. is an employee and a stock/shareholder of Novo Nordisk A/S. W.L. and L.P. are employees of Novo Nordisk (China) Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd. T.H. is on an advisory panel and is a speakers' bureau member for Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, AstraZeneca and Merck Serono, is on an advisory panel for Merck Sharp & Dohme, and is a speakers' bureau member for Eli Lilly and Bayer. W.Y., J.M., M.L., H.M., Y.P., C.W., X.X., T.Y. and Z.W. have no conflicts of interest to declare. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th ed. 2017. http://www.diabetesatlas.org. Accessed November 8, 2018.
-
- Countryeconomy.com. Population China 2013: Increases in Chinese population. 2013. https://countryeconomy.com/demography/population/china?year=2013. Accessed November 8, 2018.
-
- Federation ID . IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th ed. (China report). 2017. https://reports.instantatlas.com/report/view/704ee0e6475b4af885051bcec15.... Accessed November 8, 2018.
-
- American Diabetes Association . 4. Lifestyle management: Standards of medical care in diabetes‐2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S38‐S50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

